The development and changes of armor protection technology are in line with the development of new warheads, and are the product of the spiral promotion of protection and damage. The emergence of new damage weapons such as tandem armor-piercing warheads, kinetic warheads, self-forging warheads and intelligent terminal-sensitive bombs has enriched the means of war. In fact, with the development of anti-tank weapons and the change of battlefield environment, the current armor protection technology faces the following prominent problems and contradictions: on the one hand, the armor-piercing ability of modern anti-tank weapons has been greatly improved, and informationized ammunition and roadside bombs can also attack from all sides of the tank; on the other hand, in order to meet the needs of rapid mobility and long-range delivery, the next generation of armored vehicles must be lightweight. Therefore, how to significantly reduce the weight of tanks and armored vehicles while maintaining and further improving the protection capabilities of vehicles to counter the growing development of anti-armor weapons has become a new challenge facing armor protection technology. Passive electromagnetic armor protection technology is considered to be expected to meet this challenge.
What is passive electromagnetic armor?
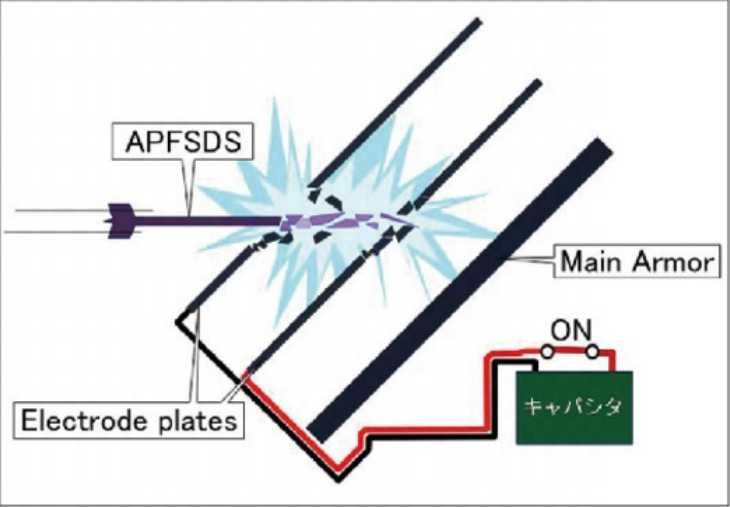
Since 1973, American scholar Walker Neil proposed the idea of using the ohmic heating effect of electromagnetic fields on current-carrying metal jets to reduce the penetration ability of jets, a new type of additional protection system, electromagnetic armor, came into being, proposing a new solution to the special requirements of main battle tanks and other armored vehicles for lightweight and impact resistance. Generally speaking, electromagnetic armor is a new type of additional armor that uses electromagnetic energy to interfere with, intercept and destroy incoming shells to reduce or eliminate the destructive power of shells. From the perspective of the defense method of electromagnetic armor, electromagnetic armor is divided into active electromagnetic armor and passive electromagnetic armor. Active electromagnetic armor has evolved from traditional active protection technology. It uses electrical energy to generate a magnetic field instead of chemical energy to launch an interception plate. The interception plate collides with the incoming shells, destroys the shells or destroys the trajectory, reduces the destructive power of the shells, and achieves the purpose of protecting the main armor. Passive electromagnetic armor is mainly composed of two plates and energy storage capacitors at a certain distance. The two plates are connected to the two poles of the energy storage capacitor respectively. When the incoming shell penetrates the outer plate and gradually approaches the inner plate, the air gap between the shell head and the inner plate is penetrated. The capacitor begins to release electrical energy, and a strong magnetic field is generated between the two plates. A strong current flows through the projectile and is acted upon by the Ampere force, thereby causing the projectile to deflect, bend, or even break, thereby achieving the purpose of protecting the main armor. The simple principle of passive electromagnetic armor is that during non-critical defense and power charging, the switch is in the disconnected state to ensure the safety of the system. At the critical defense moment after charging, the switch is closed, but the circuit is still in the disconnected state. After the incoming shells penetrate the two armor plates, the circuit is turned on and begins to discharge, so the incoming shells act as a switch to connect the circuit.
In the late 1970s, the Soviet Lavdiev Institute of Fluid Mechanics first began research on electromagnetic armor. The first batch of tests was completed in January 1975, and a comprehensive study on the effects of electromagnetic and strong current on the stability of the jet of shaped charge was started. After the Gulf War in 1992, the US Army Laboratory included electromagnetic armor in the list of 21 "Key Technology Plans of the Department of Defense" submitted to Congress to strengthen research and development.
Protection mechanism of passive electromagnetic armor
As mentioned above, the earliest idea of passive electromagnetic armor was to use the Ohm heating effect to vaporize the jet to achieve the purpose of protection. The ohmic heating vaporization effect is a phase change process based on electric explosion. When the shaped charge jet hits the plate, the charge liner is squeezed by the impulse of the explosive to produce a high-pressure, high-speed metal jet. The jet eventually penetrates the two metal plates and conducts the circuit. Since there is a strong current in the jet after the circuit is turned on, a large amount of Joule heat will be generated on the jet, and the phase change process of liquid-gas-plasma, i.e. electric explosion, will be completed in a very short time. The phase change process is accompanied by strong light shock waves, electromagnetic radiation, and a sharp increase in resistance. However, although people later tried to study the vaporization problem of the jet from the perspective of ohmic heating in experiments, in order to vaporize the jet in a short time and realize the phase change process, a high amount of energy needs to be injected, which places high demands on the energy storage module and the ability of the equipment to carry strong currents. At this stage, compared with the instability of the jet, the Ohm heating vaporization effect can only be used as an auxiliary factor to analyze the reduction of the jet penetration ability. Therefore, people’s research on the protection mechanism of passive electromagnetic armor has turned to the protection mechanism of jet instability.
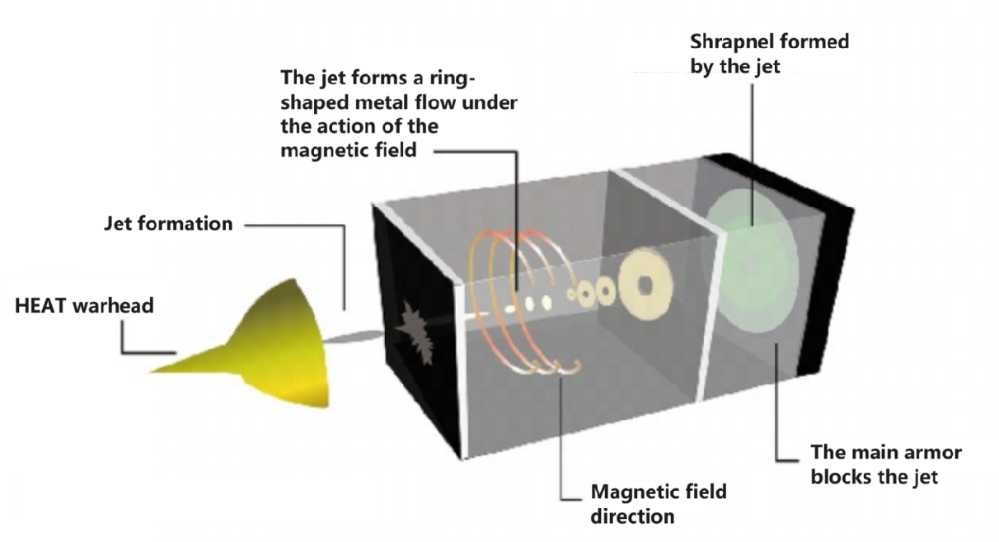
It is generally believed that the main mechanism of passive electromagnetic armor is the jet instability protection mechanism, that is, the unevenness of the magnetic field is used to make the jet particles have different gyration radii in the magnetic field to produce particle drift. After the positive ions and negative electrons in the jet gyrate in opposite directions under the action of the magnetic field, the positive and negative charges are separated, thereby affecting the stability of the jet. At the microscopic level, the effect of the magnetic field on the positive ions and electrons will be manifested as the effect of the magnetic field on the jet at the macroscopic level. When a current passes through a metal jet, it will generate an angular magnetic field that pinches the jet, which is the pinch effect. Due to the temporal and spatial inhomogeneity of the magnetic field between the plates, charged particles will move from the strong side of the magnetic field to the weak side. When there is a slight bend in the jet axis, the deformation will be gradually amplified under the action of the magnetic field, resulting in "twisted" instability; if the jet cross section is uneven and there are thick and thin sections, the magnetic field will make the thin section thinner (due to the thinning of the cross section, the jet resistance will increase, improving the effect of ohmic heating and magnetic field, aggravating jet damage), cutting off the jet, that is, "cut-off" instability (or "sausage" instability). Among the jet instability protection effects of passive electromagnetic armor, the research of the Russian Lavrentyev Fluid Mechanics Laboratory is the most representative. The laboratory conducted experiments on current-carrying jet columns with diameters of 30 mm, 50 mm, and 100 mm, and mainly obtained the following conclusions: When powered on, the jet produces an obvious necking effect and is divided into fragments; the axial length of the fragmented jet element is 1 to 3 times the initial diameter, and the radial scale is 5 to 10 times the radial scale without current; the penetration ability of the jet is significantly reduced when powered on.

In the 1980s, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory used 30mm and 50mm caliber armor-piercing shells to conduct principle test research on electromagnetic armor (peak current reached 450 kiloamperes). With standard armor plates as targets, the penetration depth of 30mm diameter was reduced from 140mm to 40mm, and the penetration depth of 50mm diameter was reduced from 220mm to 80mm. Subsequently, the Fraunhofer Institute conducted experimental research on 44mm caliber armor-piercing shells. The test results showed that the jet was significantly deformed when the current passed through, and the penetration depth of the jet decreased significantly in the three tests conducted. In 2007, in order to evaluate the protective potential of electromagnetic armor, the Netherlands Ballistic Research Laboratory conducted a live-fire shooting test of shaped charges. The measurement results also showed that the jet instability was more obvious under the action of current, so the penetration ability of the jet was reduced. In addition, the protective effect of passive electromagnetic armor is also closely related to the mechanism of lateral electromagnetic force. The mechanism of electromagnetic force is mainly to use the inter-polar magnetic field to generate lateral force on the object, causing it to shift or deflect laterally, dispersing the position where the object hits the plate, and preventing the object from hitting the plate vertically, thus playing the role of protective armor. The greater the deflection angle of the object between the poles, the smaller the attack energy density of the armor plate will be.
Passive electromagnetic armor structure and key technologies
Passive electromagnetic armor mainly includes three types: contact electromagnetic armor, electric heating armor, and energy storage electromagnetic armor. The contact electromagnetic armor is composed of two steel plates, a power supply and a capacitor bank at a certain distance outside the main armor of the land combat platform. One of the steel plates is grounded, and the other is connected to the high-voltage end of the capacitor bank. Its basic working principle is: when the incoming shells penetrate the two steel plates, the two steel plates are short-circuited. At this time, a loop is formed between the incoming shells, the two steel plates and the capacitor bank, and the capacitor bank begins to discharge; the strong magnetic field formed by the large current discharge and the discharge explosion shock wave interact with the charged incoming shells, causing the incoming shell jet to produce unstable magnetohydrodynamic phenomena, resulting in the dispersion or deflection of the incoming shell jet, thereby avoiding the main armor from being penetrated or destroyed.
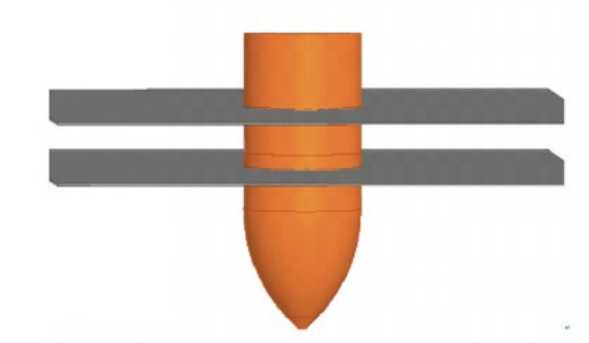
The structure of the electrothermal armor is similar to that of the electromagnetic armor, and is also composed of two metal plates, a power supply and a capacitor bank. The distance between the two metal plates is very small and is isolated by a very thin layer of insulating material. When the incoming shells penetrate the two metal plates, the power supply or capacitor group discharges a large current through the incoming shells. At this time, the insulating material between the two metal plates is heated and vaporized and expands rapidly, pushing the two metal plates to the sides, thereby interfering with the penetration of the incoming shells into the main armor of the land combat platform.
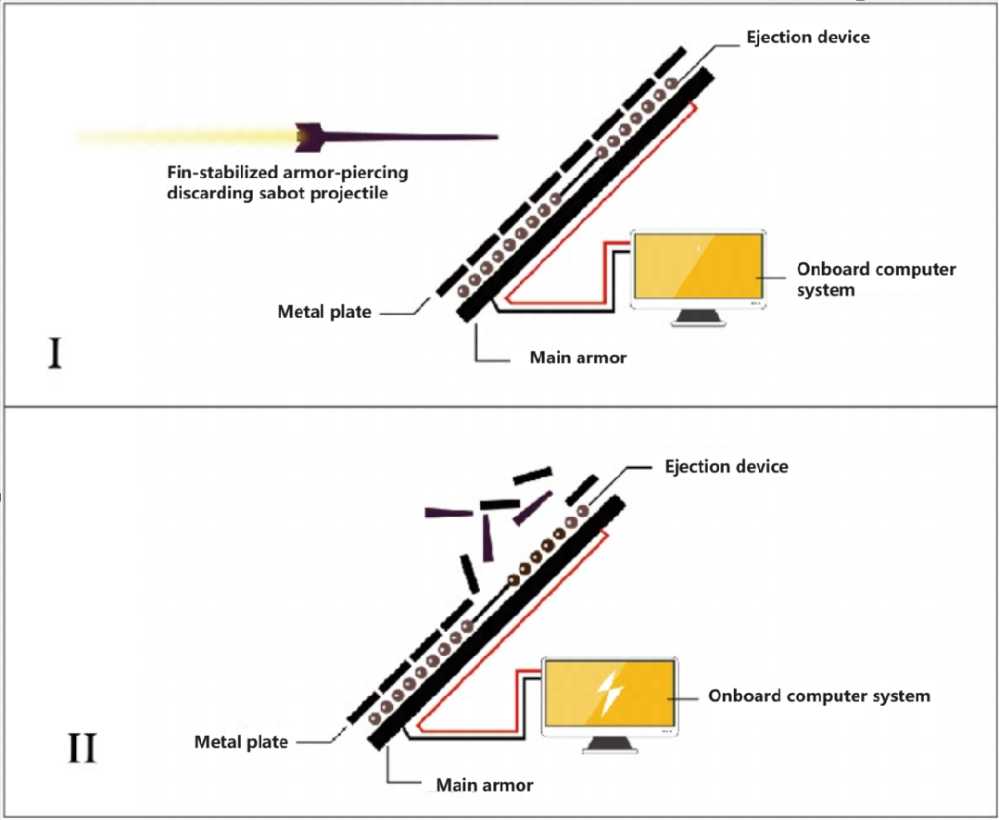
Energy storage electromagnetic armor is a new concept armor protection technology that combines the characteristics of electromagnetic armor and electric thermal armor. The energy storage electromagnetic armor unit consists of a panel, a protective plate, a bottom plate, a high energy storage density pulse capacitor, a positive and negative electrode lead wire explosive conductor switch, etc. It is both an energy storage device and a protective device. Each energy storage electromagnetic armor unit is fixed to the main armor by bolts, connected in parallel and connected to a high-voltage cable, and charged by the charging device of the fully electrified land combat platform. When the jet of armor-piercing shells or the kinetic energy rod of armor-piercing shells hits any energy-storing electromagnetic armor unit, the insulating layer between the two electrodes of the capacitor will be destroyed, causing a short circuit between the positive and negative plates. All parallel capacitors will discharge through the short circuit. The large current generated by the discharge will first vaporize the thinner metal foil electrode in the capacitor, and then generate high-temperature plasma. At this time, other substances in the capacitor will also vaporize, expand, explode and generate shock wave pressure under the action of high temperature, pushing the protective plate to move along the outer normal direction and hit the incoming shells, causing the incoming shells to deflect or even break, thereby protecting the main armor of the land combat platform

Compared with traditional passive armor protection technology, passive electromagnetic armor has the following advantages: First, it is light in weight. The protection capability of electromagnetic armor is independent of the thickness of the armor plate. When providing the same protection capability, the weight of electromagnetic armor is only 30% or even less than that of rolled homogeneous steel armor, which greatly reduces the weight of the tank and improves its mobility and battlefield survivability; second, it is low in cost, relying on electrical energy rather than material properties to provide protection, and the manufacturing of protective plates is simple and convenient. Low cost; the whole vehicle shares a set of high-power pulse power supply. Within a certain range, the weight of the power supply will not increase with the increase of the protection area. Its initial energy is also provided by the internal combustion engine, which is cheap; third, the protection capability is high. The response speed of electrical energy is higher than the reaction speed of chemical energy. The energy passing through the current within a certain volume range is also much higher than the chemical energy. Therefore, the power density of electromagnetic armor is several orders of magnitude higher than that of explosive reactive armor, which greatly improves the protection capability; fourth, it can be repeatedly protected. As long as the incoming projectile does not cause a short circuit in the electromagnetic armor plate, as long as the high-power pulse power supply is recharged, it can continue to resist the invasion of foreign projectiles; fifth, it is highly safe. The electromagnetic armor system does not contain flammable and explosive items such as explosives and oil, and the safety performance in production, transportation and storage is higher.
At present, there are some key technical thresholds that need to be broken through for passive electromagnetic armor to achieve its goals, such as high-voltage capacitor group technology. Electromagnetic armor must be composed of a high-power pulse power supply composed of a pulse capacitor group with high energy storage density to provide electrical energy. Although it is generally believed that a current greater than 300 kiloamperes can significantly reduce the penetration of armor-piercing shells, to protect against rockets and anti-tank missiles currently in common use, a current of at least 1 megaampere is required, and the energy storage of the pulse capacitor must reach at least 1 to 2 megajoules. The energy required for electromagnetic armor to work is relatively large, so a large number of on-board capacitor banks are naturally required, which increases the overall mass and volume of the fully electrified land warfare platform, and in turn affects its driving performance and maneuverability. For this reason, the research on high specific energy storage device technology is very necessary to improve the specific energy of the energy storage device and reduce its impact on the mobility of the land combat platform. In September 2003, the British military played a video clip to the scholars and military personnel attending the "SMi Combat Vehicle Survivability Seminar" held in London. The content was the anti-ballistic performance shooting test of the "Warrior" infantry fighting vehicle test vehicle equipped with electromagnetic armor. The video shows that an RPG-7 anti-tank rocket was fired at the "Warrior" infantry fighting vehicle from the side at a close distance. A huge ball of fire and thick smoke instantly emerged from the side of the vehicle, showing the huge power of the rocket. However, before the fireball and thick smoke dissipated, the "Warrior" infantry fighting vehicle test vehicle was at ease. It drove away from the demonstration area. This shows that the main armor of the tank was not damaged, the electromagnetic armor withstood the severe test, and the test achieved initial success. The whole set of electromagnetic armor is composed of bulletproof metal plates (electrode plates), insulating plates, power distribution lines, capacitors of pulse power supply, etc. In the static shooting test, the pulse power supply capacitor is powered to form a high-voltage electric field of several thousand volts. At the moment when the RPG rocket hits the electromagnetic armor, the circuit is turned on, forming a super strong current and electromagnetic field, which disperses and cuts off the metal jet of the rocket. In this way, even if the electromagnetic armor is partially damaged, the main armor of the "Warrior" tank is safe and sound. This live-fire shooting test shows that the British may have made a major breakthrough in the development of electromagnetic energy storage devices.
In addition, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and the Army Tank Power Research, Development and Engineering Center have started the design of compact high-power pulse power supply and electromagnetic armor test work since 2000, and designed and developed the electromagnetic armor test platform and electromagnetic armor test module. On February 22, 2005, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and the Army Tank Power Research, Development and Engineering Center completed the integrated research of electromagnetic armor module and hybrid electric drive vehicle. Live-fire shooting tests were conducted at the Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland. In the field shooting test, the electromagnetic armor module installed on the hybrid electric drive demonstration vehicle successfully resisted multiple incoming ammunition, which seems to indicate that the United States has made a major breakthrough in the development of vehicle-based electromagnetic energy storage devices.
There are two main general design ideas for electromagnetic energy storage devices (PFN) for ground armored combat platforms: small energy storage capacity modules (the rated energy storage of a single module is generally not more than 300 kilojoules) and large energy storage capacity modules (the rated energy storage of a single module is generally greater than 1 megajoule). At present, the industry generally adopts small energy storage capacity module structure design for open experiments. When the total amount of system energy storage is certain, the PFN composed of small energy storage capacity modules is more conducive to the precise adjustment of the output current waveform and easy to match the ideal working current for the transmitter. However, even so, reducing the module volume, increasing the module energy storage density, and improving the module miniaturization technology level have long been a key content of pulse power supply technology research at home and abroad. To achieve the miniaturization of the module, first of all, there must be miniaturized high-power components available, and secondly, the module must have a compact structure. The current research objects of high-power component miniaturization mainly include metallized film capacitors, high-power thyristors, etc.; the research content of module structure compactness mainly includes conductive structure miniaturization, insulation structure miniaturization, etc. The module miniaturization technology level and research results are intuitively reflected in the energy storage density. In this regard, the United States has the highest research level, far ahead of other countries. As early as the 1990s, the United States began to conduct research on the miniaturization of high-power components and the compactness of module structures. In the research on the miniaturization of metallized film capacitors, the energy storage density of the mature technology components developed by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the United States in 2010 was only 0.68 MJ/m3: in 2014, the energy storage density of the mature technology components developed by General Atomics in the United States reached 4 MJ/m3, and the energy storage density of laboratory samples was as high as 7 MJ/m3. In the research on the miniaturization of high-power thyristors, in 2001, Silicon Energy Corporation of the United States studied the sandwich semiconductor packaging technology and successfully reduced the thickness of the components of high-power thyristors. In the research on the compactness of module structures, in 2017, the International Physics Corporation of the United States developed a PFN with an energy storage density of up to 1.2 MJ/m3 for electrothermal chemical guns; currently, the United States has begun to develop a PFN with an energy storage density greater than 4 MJ/m3. In addition to the miniaturization and high energy density technology of high-voltage capacitor banks, the thermal management technology of heavy-frequency continuous firing is also a technical threshold that must be overcome for the practical application of passive electromagnetic armor. As a component that provides transmission energy, PFN must have the ability to work with heavy-frequency continuous firing corresponding to the radio frequency of electromagnetic armor. However, due to the existence of internal resistance, part of the electrical energy will be converted into heat and distributed in the high-power components during the module pulse discharge, and under the discharge condition of load short circuit, the stored electrical energy will be almost completely converted into the internal heat of the module. The compact structure makes the internal space of the module very small, and the high-power components need to adopt an insulating and sealed structure, which is not conducive to the internal heat dissipation. Continuous discharge under high radio frequency will cause heat to accumulate quickly inside the module, causing the internal temperature of the component to rise sharply, and then insulation overheating damage will occur, and electric thermal breakdown failure will occur. Obviously, the higher the level of PFN miniaturization technology and the more compact the module structure, the more prominent the heating problem will be when working with repeated and frequent bursts.

The high-power components that are easily damaged by heat accumulation mainly include pulse inductors, pulse switches and freewheeling silicon stacks. In addition, energy storage capacitors usually do not suffer from overheating damage. The main reason is that they are composed of many single core components connected in series and parallel. The internal heat generation is relatively uniform, without a concentrated point. At the same time, the volume and mass are relatively large, and the heat capacity is large. However, the pulse inductor designed by miniaturization process has high energy storage density and small volume. The current-carrying coil is generally cast and encapsulated with epoxy resin insulation materials. The thermal conductivity of epoxy materials is very low, so the heat of the coil is difficult to dissipate outward, which can easily cause the surrounding insulation to be overheated and damaged, resulting in inter-turn short-circuit faults. The pulse switch is composed of high-power thyristors in series, and the freewheeling silicon stack is composed of high-power rectifiers in series. The heat of these semiconductor components is mainly generated on the silicon wafer located in the center of the component. Because the component tube core is encapsulated in a ceramic tube shell, the heat needs to be conducted and dissipated to the outside through the molybdenum sheets and metal tube covers on the upper and lower sides. However, in the structure of multiple components in series, the tube covers are closely connected, so the heat inside the tube core cannot be quickly dissipated to the outside, which can easily cause thermal stress damage to the lattice of the silicon wafer. Therefore, reliable thermal management technology is the basic premise and fundamental guarantee for the engineering of passive electromagnetic armor for pulse power supply equipment.

Prospects for the practical application of passive electromagnetic armor
Discussing the prospects for the practical application of passive electromagnetic armor is actually a complex topic, not only because of the technical threshold of passive electromagnetic armor itself. Through the research on electromagnetic armor protection technology in recent decades, its theory, simulation and experimental technology have made great progress, but it is also undeniable that there is still a long way to go for passive electromagnetic armor to go out of the laboratory and realize engineering military applications. For example, the results of many years of research have shown that passive electromagnetic armor can effectively defend against the metal jet of armor-piercing projectiles. However, the main reason why military applications have not yet been realized is the lack of mechanism and experimental research on armor-piercing projectiles. Although the speed of armor-piercing projectiles is lower than that of armor-piercing projectiles, their core diameter is large and the material strength is high. It is necessary to deepen the mechanism of electromagnetic armor and re-optimize the design parameters of electromagnetic armor so that it can protect both armor-piercing projectiles and armor-piercing projectiles. Only in this way can the practical application process of electromagnetic armor be promoted. It is also necessary to see that, compared with traditional protection systems, passive electromagnetic armor has the advantages of light system weight, effective resistance to armor-piercing shells and multiple strikes.
However, in order to play its protective role, it must also be integrated with the basic armor to solve engineering problems such as insulation and support, integrated wiring and power integration. Therefore, strengthening system integration research will be one of the development focuses of electromagnetic armor. In fact, after the European Seminar on Electromagnetic Armor held in March 2009, the European Defense Agency has launched a project to study the practical application of passive electromagnetic armor for armored vehicles, focusing on the comprehensive integration research of electromagnetic armor. After more than ten years of continuous investment, significant results have been achieved by 2023. In addition, for tank armored vehicles, their body, turret or chassis serve as power ground, signal ground and safety ground. However, electromagnetic armor works under high voltage, high current and strong magnetic field environment. Even if there is milliohm resistance at the ground end, it will generate thousands of volts of voltage. At the same time, the strong magnetic field will be coupled to the inside of the vehicle through the vehicle body. Therefore, the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of electromagnetic armor are one of the key technologies for its military engineering application. To this end, the European Defense Agency has also begun to study the safety criteria for the use of electromagnetic armor, including establishing safety and risk assessment methods for the operation, maintenance, training and storage of electromagnetic armor, assessing the general functions and inherent hazards related to the performance of electromagnetic armor and the possible impact of these hazards, establishing a safety assessment process for identifying potential hazards, formulating safety standards, etc., and formulating corresponding research plans.
Finally, one of the main problems is that since electromagnetic armor requires a strong power supply, it is unrealistic to simply install electromagnetic armor on a vehicle. It is necessary to first realize the electric drive tank, then realize the installation of electromagnetic guns, and the last step is to install electromagnetic armor on a vehicle under the overall consideration of the all-electric tank. It can be said that the day when electromagnetic armor is installed is the day when all-electric tanks are realized. The full electrification of land warfare platforms refers to using electricity as the basic energy source, and converting electricity into another form of energy through technologies such as transmission, conversion, control, and distribution of electricity, or using electricity efficiently to achieve the optimal operation of various systems of the land warfare platform and the overall improvement of the overall performance of the land warfare platform, especially the improvement of tactical and technical performance in power drive, weapon system, and protection system. Compared with traditional land warfare platforms, all-electric land warfare platforms have a larger precision firepower strike range, more comprehensive comprehensive protection capabilities, faster mobile assault capabilities, and more efficient battlefield perception capabilities. They have also made great improvements in terms of controllability, concealment, and human-machine environment, and are convenient for mobile deployment and logistics support. Therefore, with its comprehensive performance and combat capabilities that are superior to traditional land warfare platforms, all-electric land warfare platforms have become the focus of investment and research by the world’s military powers, and will inevitably become the development direction of future army equipment and the research hotspot of future land warfare platforms.

It should be pointed out that the current practical development of all-electric tanks and land armored combat platforms, in addition to the key technologies involved in drive motor technology such as high-power density motors, motor thermal management and cooling methods, and permanent magnet motors with special structures, mainly focuses on the research and development of integrated power systems for all-electric land warfare platforms. The integrated power system of the fully electric land warfare platform refers to a vehicle-mounted integrated power system that uses engine-generator sets, power batteries, supercapacitors, etc. to provide power for drive motors, electromagnetic armor, electromagnetic weapons, etc. Its advantages are high energy utilization, high mobility, diversified power supply capabilities, flexible layout, and the ability to conduct covert operations. The integrated power system of the fully electric land warfare platform can operate in a single vehicle island, or it can be connected to the grid with other fully electric land warfare platforms to achieve interaction and energy sharing. In the grid-connected mode, a single platform can serve as an energy guarantee node: it is both a battlefield energy consumption unit and a battlefield energy storage unit, thus forming a battlefield smart grid. The key technologies of the integrated power system of the fully electric land warfare platform include power supply and distribution (power generation and storage subsystem), power conversion (power conversion subsystem), power management (management and control subsystem), etc. Among them, in addition to power distribution, the difficulty of power conversion and power management technology is easily overlooked. The power conversion subsystem can realize energy conversion and energy management of the fully electric land warfare platform system. As the core unit of system energy conversion and important executive components of system energy management, bidirectional DC/DC converter and pulse width modulation (PWM) rectifier are the research focus of power conversion subsystem. Power management includes integrated management control unit, system energy management, power quality analysis and management. According to the system status information, the integrated management control unit can send control instructions to the engine controller, PWM rectifier, power battery management system, bidirectional DC/DC converter and other components and devices as well as various high-voltage contactors inside the system to control their coordinated work. In order to ensure the stable and healthy operation of the system, the control logic of the integrated management control unit is complex and the amount of calculation is large. At the same time, it has high requirements for real-time anti-interference ability and fault tolerance. System energy management can realize the coordinated control between various energy sources, adapt them to the load characteristics, and meet the power demand of each subsystem to the maximum extent. At the same time, under the premise of realizing the above functions, the system energy management can also control each energy source to operate in the optimal or suboptimal working mode to improve the system working efficiency and extend the service life. For example, control the engine to work in the high-efficiency area of fuel efficiency, maintain the power battery SOC in the high-efficiency area of charging and discharging and reasonably control the charging and discharging process, and reasonably plan the bus voltage to improve the utilization rate of supercapacitors. The key technologies of system energy management also include power division of high-frequency transient components and low-frequency components of system power demand, low-frequency power distribution, state planning of bus voltage and distribution power correction, etc. In addition, there are a large number of power conversion devices in the various task loads of the integrated power system of the fully electrified land warfare platform, which can easily cause grid fluctuations and affect the power supply quality. Therefore, the spectrum calculation, harmonic suppression and grid quality analysis of the system DC network current harmonics play an important role in improving power supply quality, maintaining system stability and enhancing platform performance. In short, electromagnetic armor is an important component closely related to the fully electric tank. It can be said that without the powerful electric energy provided by the fully electric tank, electromagnetic armor is out of the question. Only after achieving the key technical thresholds of the fully electrified tank can the engineering application of passive electromagnetic armor be paved.
Electromagnetic armor technology can also make tanks and armored vehicles have "body protection skills". Unlike the "hard-on-hard-on" of traditional armor, electromagnetic armor technology has a sense of "four ounces to move a thousand pounds". Passive electromagnetic armor is a new concept of additional armor that uses electrical energy to interfere with and destroy incoming projectiles to reduce and eliminate damage to the main armor, thereby improving the protective ability of armored vehicles. The protective ability of electromagnetic armor has nothing to do with the thickness of the armor plate. While providing the same protective ability, the weight of electromagnetic armor is only 30% of the rolled homogeneous steel armor, or even less, which greatly reduces the weight of the tank and improves its mobility and battlefield survivability. The response speed of electrical energy is higher than the reaction speed of chemical energy, and the energy passing through the current within a certain volume range is also much higher than chemical energy. Therefore, the power density of electromagnetic armor is several orders of magnitude higher than that of explosive reactive armor, which greatly improves the protective ability. There are no flammable and explosive items such as explosives and oil in the electromagnetic armor system, and the safety performance in the production, transportation and storage links is higher. Although passive electromagnetic armor technology is not mature, it has broad prospects. With the development of weapon science and technology, "all-electric tanks" will be an important development direction for tanks and armored vehicles, and it is natural for electromagnetic armor to become a part of future tanks. As a new concept of protection technology, electromagnetic armor is expected to provide lightweight and omnidirectional protection for the new generation of tanks and armored vehicles due to its unparalleled power density and response time.

Conclusion
As a new generation of additional protection system, passive electromagnetic armor has the advantages of light weight, rapid response, low cost, good maintainability, strong protection capability, and compatibility with future all-electric systems compared with traditional armor protection technology. It is an important development direction of future armor protection technology. As a protective structure with development potential, passive electromagnetic armor has good adaptability to future all-electric land warfare platforms and main battle tanks. With the development of weapon science and technology, all-electric combat vehicles equipped with electromagnetic guns and electromagnetic armor will be an important development direction of tank armored vehicles. Centralized management and distribution of all-electric weapons and protective equipment through an integrated energy management system will greatly improve the utilization rate of pulse power supply, reduce volume and weight, and achieve "seamless" connection with the information system to form a new generation of weapon platform. In addition, although electromagnetic armor was born around the protection of armored vehicles, as its mechanism and test technology mature, it will also be applied to the protection of other military platforms, such as the protection of underground important targets against earth-penetrating bombs. At this time, the volume and weight of high-power pulse power supply will not be limited. Similarly, there is enough space on ships to install pulse power supply. It can also be used for the protection of space targets. Especially for ultra-high-speed (3-10 km/s) and small-sized (millimeter-level) space debris, electromagnetic armor will be able to give full play to its advantages of fast response speed and large power pulse. For example, in 2009, the Russian Institute of Applied Machinery and Electric Drives used the principle of electromagnetic armor to conduct electromagnetic protection tests on spacecraft, using electromagnetic armor plates with metal wires to simulate the protection process of orbital debris. It can be foreseen that passive electromagnetic armor will also be tested and applied on various weapon platforms.





















