This article is a discussion by a Chinese scholar on the development of aircraft carriers in the era of stealth aircraft. His conclusion is that the current space reconnaissance system has been perfected, stealth fighters and long-range hypersonic missiles have been equipped to the troops, and the effectiveness of aircraft carrier formations in wars between powerful countries has been greatly reduced. Aircraft carrier battle groups can only deal with small and medium-sized countries. Therefore, the development of medium-sized aircraft carriers is more suitable for the navy of a major country to maintain regional order and is less expensive.
His views do not represent the Chinese government, and his views on aircraft carriers do not represent the Chinese people. China is now an absolute supporter of giant aircraft carriers, but his great power strategy theory represents a large number of Chinese hawkish scholars. The full text is reproduced here. It comes from the views of competitors, so please make your own judgment.
Necessary review
Since World War II, aircraft carriers have long been the core equipment for maritime operations and the symbol and cornerstone of the sea power of major countries. However, "no one is good for a thousand days, and no flower is red for a hundred days." With the development of equipment technology and combat systems, the role and status of different equipment will also change. It is impossible to prosper forever. Indulging in past experience is often extremely harmful to future wars. For example, during World War I, light rapid-fire guns based on the experience of the Franco-Prussian War were useless in the face of trenches, and large-caliber heavy artillery became the "God of War"; during World War II, the armored forces with tanks as the core, combined with the "blitzkrieg" tactics, made the Maginot Line based on the experience of trench warfare in World War I meaningless, and France, which had the world’s strongest army, quickly collapsed and surrendered; another example is that during World War II, the British aircraft carrier fleet air raided the Italian Taranto naval port, sinking an Italian Navy battleship at the slight cost of losing two aircraft, damaging two battleships, two cruisers and two auxiliary ships, and aircraft carriers began to replace battleships as the core of the world’s navy. Under certain technical conditions, there is always one or several equipment that becomes the core and foundation of the combat system. When the technology develops to a certain level, the transformation of the core equipment will inevitably lead to changes in the entire combat system, which will in turn affect the war form and the rise and fall of the country. Only by timely adapting to the development of the times and adjusting the status and usage of different equipment in a timely manner can the army better assume the heavy responsibility of defending national security and safeguarding national interests.
Historically, the military in peacetime tends to be extremely conservative in the reform of equipment and tactics systems. In many cases, it would rather purchase existing equipment types than change the direction of development. For example, after the US Navy proved the power of aircraft carriers in the "Fleet Problem" series of exercises in the early 1930s, it still purchased 10 battleships with a total standard displacement of 390,000 tons after the naval arms treaty expired and before the outbreak of the Pacific War. During the same period, it only purchased 12 fleet aircraft carriers with a total standard displacement of 320,000 tons. On the contrary, after setbacks or failures, because the old system route has been proven wrong by practice and it is difficult to continue to maintain its own vested interests, the military is more able to implement effective reforms. For example, after the Vietnam War, the US military implemented the second offset strategy with high-tech weapons as the core, which led to the glorious victory of the Gulf War. The reason for this situation is that, first, once the core equipment is chosen in the wrong direction, it will inevitably delay the construction of the army. For example, after the Franco-Prussian War, the "new school" of the French Navy advocated the development of light ships to defend the homeland, which made the once glorious French Navy fleet quickly fall behind; second, the status of core equipment is relatively stable, such as the uselessness of aircraft carriers and tanks after World War II, which was once very popular, but was eventually proved to be wrong; third, after a long period of peace, the army is inevitably bureaucratic, and the idea of not seeking merit but not making mistakes is rampant. For example, the US Air Force chose the more balanced and conservative YF-22 as the prototype of the future fighter in the early 1990s, and abandoned the YF-23 that was more in line with the needs and technological development direction after the Cold War.
The current development of technology has made weapons and equipment more and more complex, so the development time is getting longer and longer. For example, the development cycle of fighter jets has been extended from 3 to 4 years in World War II to 15 to 20 years now. At the same time, the development of equipment has made the war process faster and faster, so the time of war and war is getting shorter and shorter, such as the high-intensity regional war from 3 years in the Korean War to half a year in the Gulf War. In this case, the transformation of core equipment and war forms is difficult to be tested in war, and must be completed before the war, so it can only be tested and verified through theoretical analysis and exercise simulation. Equipment systems and wars are both chaotic and difficult to understand complex giant systems with a large number of uncertain factors. Wars, especially large-scale wars, can most effectively test all factors, while theoretical analysis and exercises can only test a few factors, so their effectiveness is far lower than war. In this case, only by proving that the old core equipment and equipment system have irreparable fatal defects can we prove that the old route has come to an end, thus making it possible to switch to a new route and prepare for new forms of war.
The author believes that under current technical conditions, the combat mode of aircraft carriers and aircraft carrier strike groups has some inherent defects, making it difficult for them to continue to undertake the task of competing for sea control in a high-intensity confrontation environment, so it is difficult to be the core equipment of modern naval warfare, and its current role is not enough to offset the high life cycle cost; aircraft carriers still have great value in medium and low-intensity confrontation environments, but the life cycle cost must be greatly reduced to have sufficient cost-effectiveness; the design idea of the US Nimitz-class and Ford-class aircraft carriers in exchange for high cost for strong combat effectiveness is outdated, and the British Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers that emphasize cheapness and versatility are more in line with the current era requirements.
The threat of stealth technology
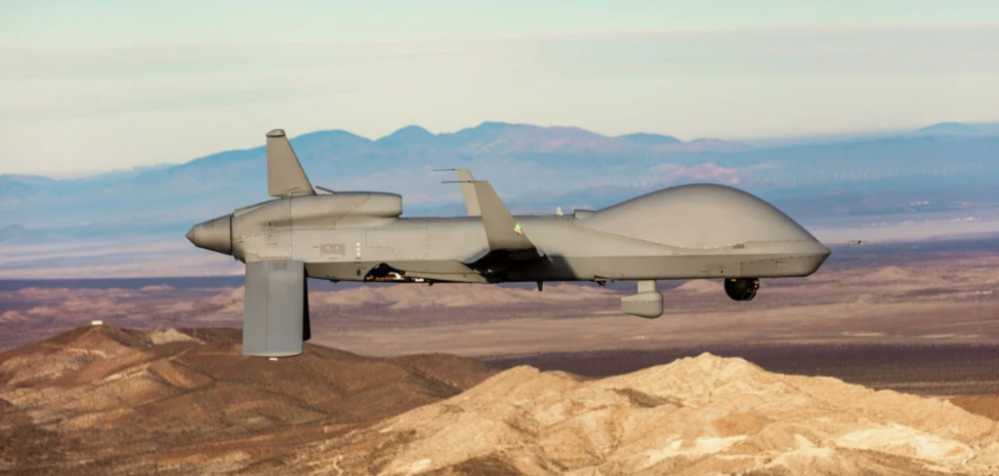
The radar stealth technology of aircraft has been put into practical use since the 1980s. In the 1990s, the F-22 stealth fighter, A-12 stealth attack aircraft, and B-2 stealth bomber had entered the engineering development stage or started to serve, marking the arrival of the stealth era of main combat aircraft, and also meaning that aircraft carriers are increasingly difficult to adapt to high-intensity confrontation environments.
During World War II and the Cold War, the threat to aircraft carrier groups mainly came from enemy attack aircraft groups. The efficiency of intercepting enemy aircraft groups can be improved by expanding the scope of the interception zone, increasing the interception firepower channel, and increasing the probability of weapon hits. The former includes deploying radar sentinel ships or early warning aircraft for long-range alert, patrolling and intercepting by our fighters, and launching long-range air defense missiles; the middle includes increasing the number of fighters and anti-aircraft guns, increasing the number of radar tracking targets, and increasing the amount of air defense missiles carried; the latter includes using radio proximity fuses, increasing the rate of fire of anti-aircraft guns, and using air defense missiles. In the middle and late stages of the Cold War, in order to improve the interception capability of Soviet reconnaissance aircraft and bombers, the US aircraft carrier group usually deployed two patrol fighters 150 to 400 nautical miles ahead of the aircraft carrier group, deployed one patrol early warning aircraft 100 nautical miles, and deployed 2 to 8 fighters on duty on standby for 5 minutes and 15 minutes on the deck to take off urgently to intercept, so as to find and intercept enemy aircraft as far as possible. The escort cruisers and destroyers were intercepted by ship-to-air missiles within 100 nautical miles. US aircraft carriers only carry a small number of short-range air defense missiles, so forward-deployed fighters and early warning aircraft are their main means of defense.
For forward-deployed fighters and early warning aircraft to intercept enemy aircraft, the fundamental premise is long-range search for enemy aircraft. Only in this way can they reliably find targets in a wide airspace and respond in time, thereby guiding fighters to intercept. Otherwise, they will not have any defensive effect at all and will be easily broken through by enemy aircraft. Before stealth aircraft entered service, the reliable detection distance of early warning aircraft for fighters, bombers, and reconnaissance aircraft was about 200 to 400 kilometers, and the tracking distance of fighters for bombers and reconnaissance aircraft exceeded 100 kilometers. The electronic reconnaissance means commonly used by early warning aircraft have a longer detection distance for targets that implement radio calls or activate search radars. Therefore, early warning aircraft can reliably and timely guide fighters carrying medium- and long-range air-to-air missiles to intercept, making it impossible for enemy aircraft to approach effective reconnaissance or attack positions, thereby protecting the safety of aircraft carrier groups.
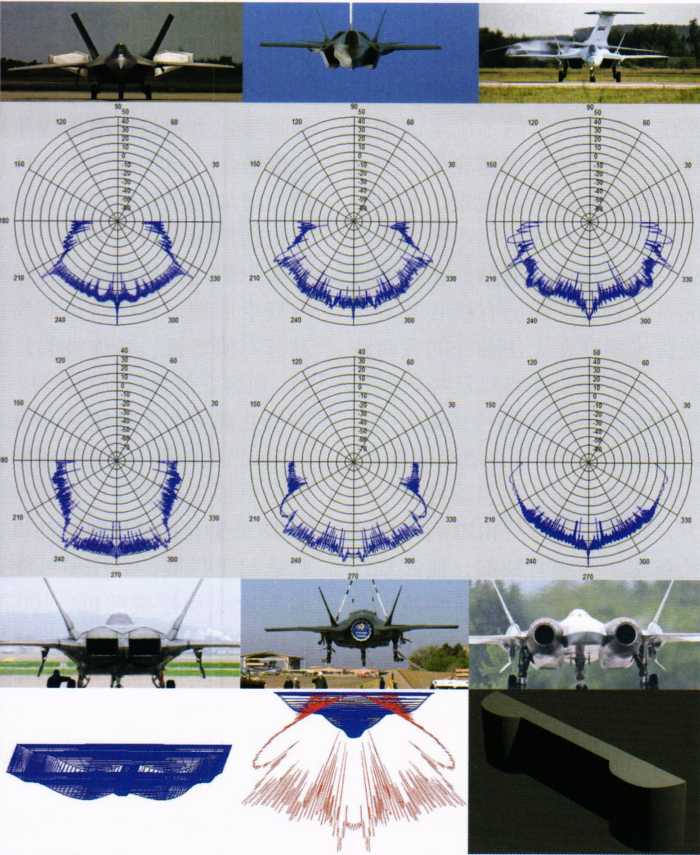
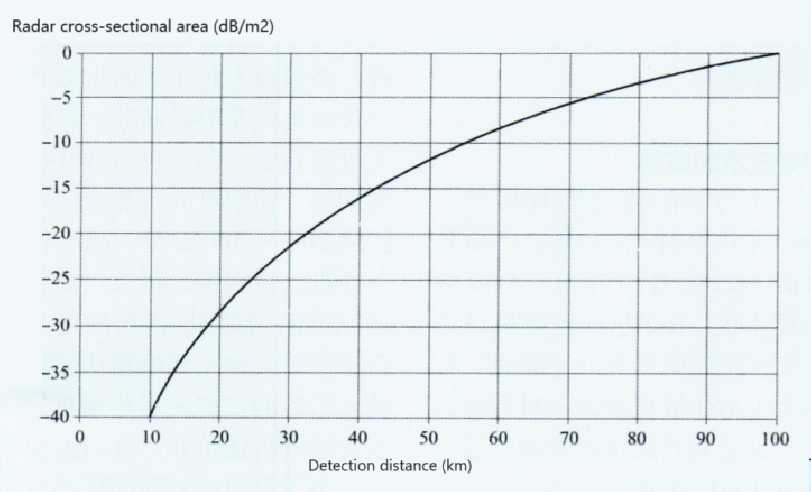
However, after the stealth aircraft entered service, the reliable detection distance of the early warning aircraft was greatly shortened. Although the decimeter wave band used by the early warning aircraft radar has a better detection effect on stealth fighters than the centimeter wave band of the fighter’s airborne radar, as long as the radar cross-sectional area of the stealth fighter drops by 25 decibels per square meter, it is enough to reduce the radar detection distance by 75%. Flying wing stealth aircraft such as A-12 and B-2 have eliminated small control rudders, and their radar stealth capabilities in the decimeter wave and meter wave bands are stronger than fighters, and they have omnidirectional stealth capabilities, making it more difficult for early warning aircraft to detect them at a long distance. If early warning aircraft and radar picket ships want to detect stealth aircraft, they must increase the radar’s power aperture product, that is, the product of the radar’s transmit power and the antenna area. However, if the radar installation platform is fixed, they can only increase the transmit power, making their own radar signals easier to be intercepted and identified by the target, so they need to plan routes in advance to avoid them. The ability to detect enemy aircraft depends only on radar performance and has nothing to do with whether the radar-carrying platform is stealth. Therefore, deploying stealth carrier-based fighters on aircraft carriers cannot change this situation.
In a relatively small area on the land battlefield, the problem of detecting stealth aircraft can be solved to a certain extent by increasing the density of radar deployment, but it is difficult for aircraft carrier groups to maintain long-range detection capabilities in this way: first, the detection and attack distance of bombers and reconnaissance aircraft to aircraft carriers is very long. Aircraft carrier groups need to find targets 500 to 600 kilometers away to effectively intercept them. The huge range of bombers and reconnaissance aircraft allows them to threaten aircraft carrier groups from multiple directions, resulting in an extremely large warning range. Many radars need to be deployed to detect targets in time; secondly, the detection distance of stealth targets is reduced, resulting in the need to increase the number of warning radars several times to maintain the same detection capability, and there are only two ways to deploy warning radars at sea: radar sentinel ships and early warning aircraft. Radar sentinel ships are expensive, and the number of early warning aircraft carried and the number of aircraft on duty at the same time are limited, and it is difficult to increase the number several times; thirdly, even if the number of radar sentinel ships and early warning aircraft is increased several times, they are easily discovered and destroyed by enemy stealth combat aircraft when deployed forward, resulting in gaps in the warning line, allowing enemy aircraft to easily cross. In this way, the significance of the forward deployment of patrol fighters, early warning aircraft and radar picket ships by the aircraft carrier group will be greatly reduced, and it will not be able to prevent enemy aircraft from discovering and attacking the aircraft carrier group, and it will not be able to maintain its own survival probability.
The basic way for the aircraft carrier group to evade enemy reconnaissance and attack is to keep a distance from the enemy, use its own combat maneuverability to hide outside the enemy aircraft reconnaissance and attack radius, and only approach the target at high speed when attacking, and release and recover the attack aircraft group at the farthest distance possible. When the United States developed the X-47B carrier-based drone, it envisioned developing a large unmanned attack aircraft with a combat radius of 4,000 kilometers based on it, so that the aircraft carrier can remain outside the enemy’s attack range. However, if the carrier-based aircraft has such a huge combat radius, it does not need to be carried by an aircraft carrier, and can achieve global coverage with only a certain number of land-based airports, and has stronger combat capabilities and higher cost-effectiveness, which has accelerated the elimination of aircraft carriers.
Before the era of stealth aircraft, land-based fighters with limited range could not conduct searches deep into the ocean. Land-based bombers and reconnaissance aircraft with longer ranges were easily detected by carrier-based early warning aircraft at a long distance, and guided by carrier-based fighters to intercept them. Therefore, the aircraft carrier group only needed to keep a distance to avoid their threats. Only after the aircraft carrier group entered the combat range of land-based fighters, the enemy could use fighters to cover bombers and reconnaissance aircraft to force a breakthrough, thereby effectively threatening the aircraft carrier group. In the era of stealth aircraft, land-based bombers and reconnaissance aircraft with longer ranges are difficult to be detected at a long distance, and can conduct effective reconnaissance and strike operations deep into the ocean alone without being restricted by the range of escort fighters, making it difficult for aircraft carrier groups to rely on combat mobility to maintain their survivability.
The threat of aerospace technology
The survival of aircraft carrier groups mainly depends on concealment. Satellite reconnaissance has the largest coverage and the best field of view, and is not threatened by carrier-based aircraft and anti-aircraft missiles. It is the best means to search for aircraft carrier groups. During the Cold War, the Soviet army deployed US-A radar reconnaissance satellites and US-P electronic reconnaissance satellites to search for US aircraft carrier groups. Limited by the times and technical capabilities, both are easily interfered by US electronic countermeasures and difficult to identify false targets; the high price makes their number extremely limited, and it is difficult to quickly cover a large area of sea, so it cannot become a reliable and effective reconnaissance means. The current development of satellite and rocket technology has rapidly improved space-based reconnaissance capabilities, solving various problems that existed during the Cold War, making it difficult for aircraft carrier groups to maintain their concealment.
The development of optical technology enables synchronous orbit satellites to have a ground resolution of 10 to 50 meters, and low-orbit small satellites weighing hundreds of kilograms have a ground resolution of 1 meter. At the same time, the development of automatic image recognition technology has greatly improved the speed of satellite image interpretation. The combination of the three enables space reconnaissance to quickly discover large ships and accurately identify the types and models of ships, making it impossible for aircraft carriers to hide. The development of radar technology enables small synthetic aperture radar reconnaissance satellites weighing hundreds of kilograms to accurately identify aircraft carriers, thereby achieving all-weather and all-day searches. The application of reusable rockets can greatly reduce the cost of satellite launches. The development of semiconductor technology and ion rocket engine technology has reduced the weight of reconnaissance satellites from several tons during the Cold War to hundreds of kilograms. The unit price of satellites has also dropped significantly, making a qualitative leap in the number of satellites deployed in orbit and their reconnaissance capabilities.
For example, my country’s "Jilin-1" series of high-resolution satellites have achieved a network of 46 satellites in orbit in early May 2022, and will achieve a network of 138 satellites by the end of the "14th Five-Year Plan", with the ability to revisit any location in the world within 10 minutes, with a maximum resolution of 0.72 meters; the "Gaofen-4" synchronous orbit reconnaissance satellite put into use in June 2016 has a ground resolution of 50 meters, and each photo covers an area of about 160,000 square kilometers, covering the Western Pacific region in 4 to 12 minutes; the "Gaofen-3" synthetic aperture radar satellite launched in August 2016 has a maximum resolution of 1 to 50 meters and a width of 10 to 300 kilometers. In the foreseeable years, my country’s space-based reconnaissance network will be able to revisit any location in the world within 10 minutes, thereby continuously tracking and identifying aircraft carriers, completely losing their concealment. Even if the aircraft carrier group can use laser weapons to interfere with satellite reconnaissance, the space-based reconnaissance network can obtain the approximate location of the aircraft carrier group and guide stealth reconnaissance aircraft to conduct detailed reconnaissance.
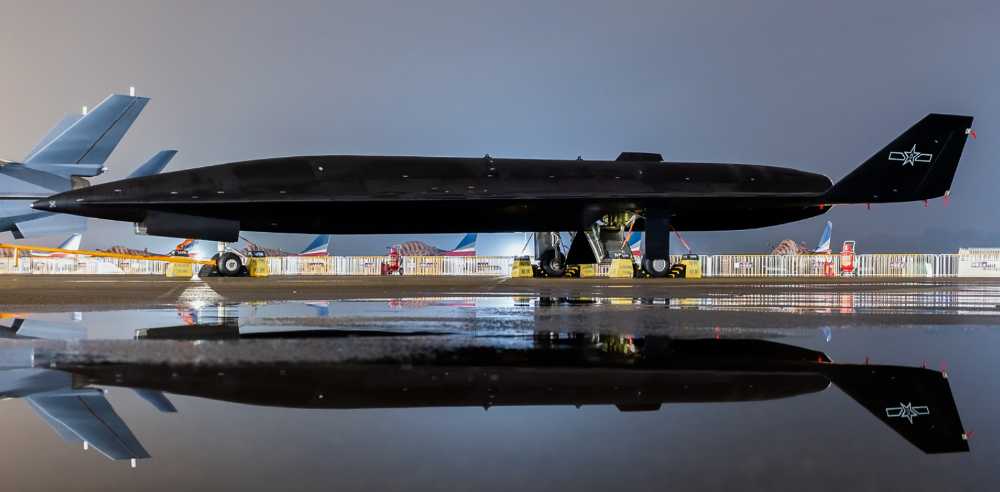
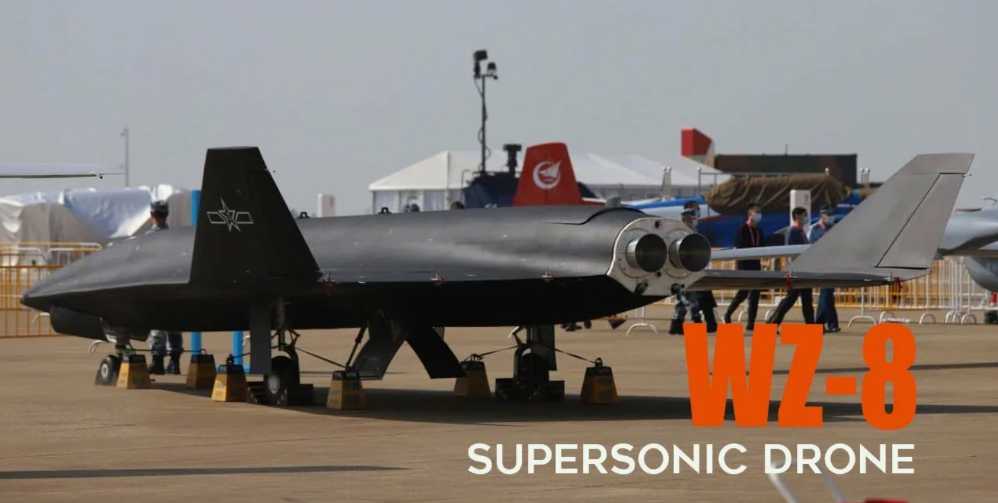
Hypersonic technology is mainly used for attack weapons such as missiles, and can also be used by aircraft to perform detailed inspections or target identification and positioning tasks. For example, my country’s Wuzhen-8 reconnaissance aircraft uses two rocket engines and can fly at a speed of more than 40,000 meters at an altitude of more than 4~5 Mach. Aircraft carrier-based aircraft cannot intercept it. Only air defense destroyers can intercept it using high-altitude interceptor missiles similar to THAAD interceptors. At present, most hypersonic anti-ship missiles are ballistic-gliding types. For example, my country’s "Dongfeng" 21D has a range of about 2,000 kilometers, far exceeding the strike range of about 1,000 kilometers for carrier-based aircraft, and can launch attacks outside the strike range of aircraft carrier groups. Hypersonic missiles fly extremely fast. A missile with an average speed of 10 Mach can fly a distance of 2,000 kilometers in just 13 minutes. It can strike the aircraft carrier immediately after the satellite determines its position. In the same period of time, the aircraft carrier group can only sail about 10 kilometers and cannot escape the search range at the end of the missile; the carrier-based aircraft cannot intercept it and must rely on the protection of air defense destroyers.



The choice of aircraft carrier development direction
From a theoretical analysis, it is only necessary to prove that there are irreparable fatal defects between the old core equipment and the equipment system, and then effectively question the old route. The old route that can overcome the doubts must be able to refute the doubts with theory. For example, the failure of the tank uselessness theory caused by anti-tank missiles is because tanks have strong campaign and tactical mobility, and can concentrate troops on one point to break through the enemy’s defense, making it impossible for anti-tank missiles to play their low-cost advantages; and when anti-tank missiles are installed on armed helicopters, fighters and attack aircraft, they have stronger mobility, and the value of tanks has dropped significantly.
To sum up As mentioned above, when current aircraft carrier groups face threats from stealth aircraft, space-based reconnaissance networks, and hypersonic weapons, their carrier-based aircraft are often helpless in defense and almost useless. If the combat radius during offense is smaller than the strike range of enemy weapons, the fleet will inevitably be passively attacked. Once carrier-based aircraft are unable to function, aircraft carriers that use them as their main means of combat will lose their meaning. Stealth aircraft, space-based reconnaissance networks, and hypersonic weapons have overwhelming advantages over aircraft carriers in terms of information acquisition, strike capability, survivability, and maneuverability. Moreover, they are not only dedicated anti-aircraft carrier weapons, but also the new cornerstone of modern warfare. They also have huge advantages over aircraft carriers in terms of life cycle costs, which makes the combat situation of aircraft carriers even more embarrassing. Aircraft carrier groups must solve their own survival problems. In order to solve the problem of insufficient storage capacity, it is necessary to solve the problem of long-range detection of stealth aircraft, deploy space-based reconnaissance and strike systems with overwhelming advantages, and greatly improve the interception capability of hypersonic weapons, which is not easy for any country to achieve in the foreseeable future. Therefore, it can be said that aircraft carriers are unlikely to become the core equipment of the naval battlefield in the future high-intensity confrontation. The route of the US Ford-class aircraft carriers in exchange for a high dispatch rate at a huge cost does not conform to the current direction of technological development and has gone astray.
The reason why the US aircraft carriers continue the route of high dispatch rates is that the naval vested interest groups are the biggest suspects. This is also the fundamental reason why the armies of various countries have repeatedly missed the opportunity for reform in different periods. The US Navy has long Taking large aircraft carriers, amphibious assault ships and nuclear submarines as the core of the army will inevitably form a very powerful vested interest group. For example, in 1995, Admiral Burda, the US Navy Chief of Operations, proposed the concept of arsenal ships, planning to purchase 5 arsenal ships with a full load displacement of 40,000 tons, 500 missile vertical launch tubes and 2 155mm naval guns, and dispatch 1~2 ships to participate in the attack in wartime, providing the "Tomahawk" missile launch capability equivalent to 1~4 single aircraft carrier battle groups. Because the arsenal ship has the potential to threaten the status of the aircraft carrier group, it is very unfavorable to the US Navy’s plan to maintain 12 aircraft carriers, so it has been opposed by many parties. On May 16, 1996, Admiral Burda was forced to commit suicide because of the hype of wearing the V-shaped medal that he did not receive. After losing its most important supporter, the arsenal ship was officially discontinued in October 1997.
In the foreseeable range, only China and the United States can be equipped with long-range stealth aircraft, space-based reconnaissance networks and hypersonic weapons at the same time. Russia, Britain, France and other countries either lack these items or are very weak in all three capabilities, and cannot establish multi-dimensional combat capabilities that can threaten ocean-going aircraft carriers. Therefore, only when China and the United States are in direct conflict, or when one of them provides strong support to a third party, will the survivability of aircraft carriers be seriously insufficient. In other cases, they are still effective combat forces. Under existing technical conditions, only aircraft carriers can provide a large number of tactical aviation forces in the airspace of enemy countries across the ocean. Only tactical aviation forces can perform tasks such as fighting for air superiority, campaign tactical strikes, and supporting landing operations, thereby effectively safeguarding national interests. Whether to continue to develop aircraft carriers depends on the judgment of the future world situation: if China and the United States fall into a comprehensive confrontation, aircraft carriers should be abandoned as soon as possible, otherwise there is still room for development.
Since the early 1980s, the United States has rapidly turned to virtual capitalism. In July 2016, the author pointed out that the United States has retreated significantly in economic globalization and released the economic ties that have maintained Sino-US relations in the past few decades. This means that the economic ties that serve as the "ballast stone" of Sino-US relations are likely to gradually weaken, the common interests of both sides will continue to decrease, and the possibility of armed conflict will increase greatly. However, judging from the performance in the past six years, the United States has entered the end of the empire. Trump has chosen to abandon economic globalization and promote the route of re-industrialization, while the Biden administration is unable to reverse the strategic direction again and is unable to promote the implementation of the re-industrialization strategy, which will inevitably lead the United States into a continuous decline. The comparison of military and other aspects of China and the United States has crossed the qualitative change point, making the US military dare not launch a war against China, and the long-term security war has made its warlord trend more obvious. The army of industrial capital only forces other countries to open their markets, and the decline after defeat is gradual; virtual capital must use violence to force physical producers to accept their own currency and financial products in order to make a profit. Therefore, the army is the core production tool of the country. A defeat will shake the purchasing power of the currency, and a sudden decline will inevitably occur. Therefore, if the war cannot be won quickly or greatly, the country will be in danger of collapse, which leads to the United States not daring to force a war when the army lacks confidence. This is also an important reason why the Biden administration is unable to reverse the strategic direction. At the same time, the United States maintains a dual advantage in overall strength and economic growth over European and American countries other than China. The benefits of transferring its own contradictions to them are higher and the risks are lower. It is not necessary to go to war with China to survive. Based on this judgment, the probability of China and the United States fighting for a long time in the future is high, and the probability of a large-scale war is low, so there is no need to completely abandon the development of aircraft carriers.
From the perspective of the world situation, the continued in-depth development of the 2008 global financial crisis has led to the collapse of the US-led economic globalization and the Yalta-old San Francisco international political system, and has caused the North Africa-Middle East and Central Asia region between the four major power core areas of the United States, Western Europe, Russia, and China to fall into continuous chaos. At present, all major countries in the world have internal contradictions that are difficult to resolve and ease. Western countries will inevitably transfer contradictions to other countries, which will cause the world situation to continue to be turbulent and regional wars to continue. my country’s development cannot be separated from the support of the world market. As the world’s largest trading country, it must have the military strength to maintain overseas markets, which requires the army to be able to win local wars of medium or larger scale thousands of miles away. To accomplish this task, developing an aircraft carrier fleet with appropriate capabilities and scale is still a necessary and efficient choice.
After the Cold War, the British Navy developed the Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carrier in response to the military needs of winning local wars and safeguarding overseas interests. Its multiple plans have abandoned the route of the US Nimitz-class and Ford-class aircraft carriers that exchanged huge costs for high sortie rates, and instead emphasized the balance between price and sortie capability, as well as the ability to adapt to multiple tasks. In the US CVNX project, various plans for conventionally powered small and medium-sized aircraft carriers were also evaluated. In a combat environment dominated by medium and low-intensity confrontations, this type of aircraft carrier obviously has a better cost-effectiveness than the Ford-class.





















