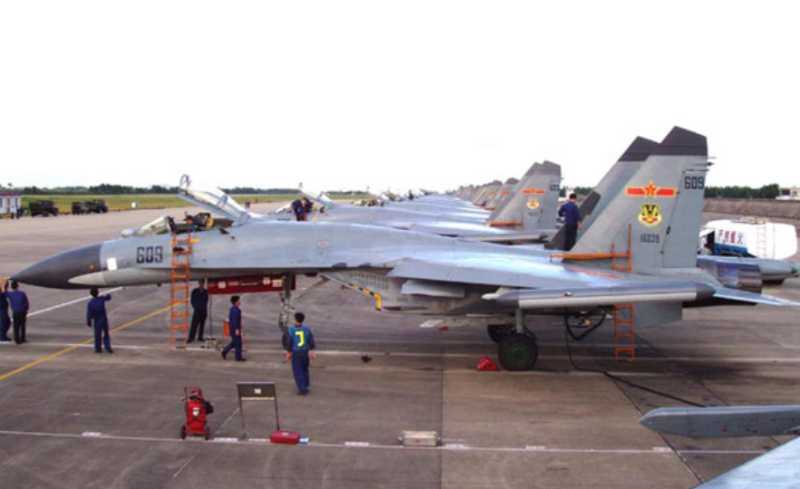
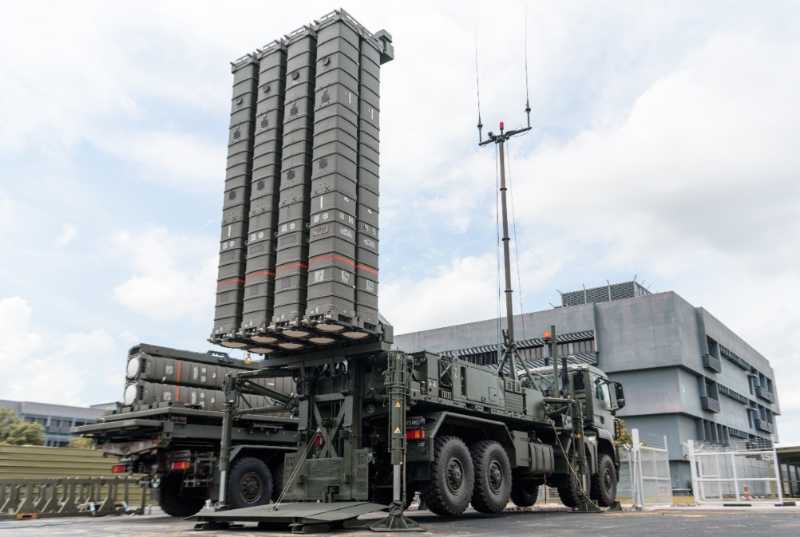
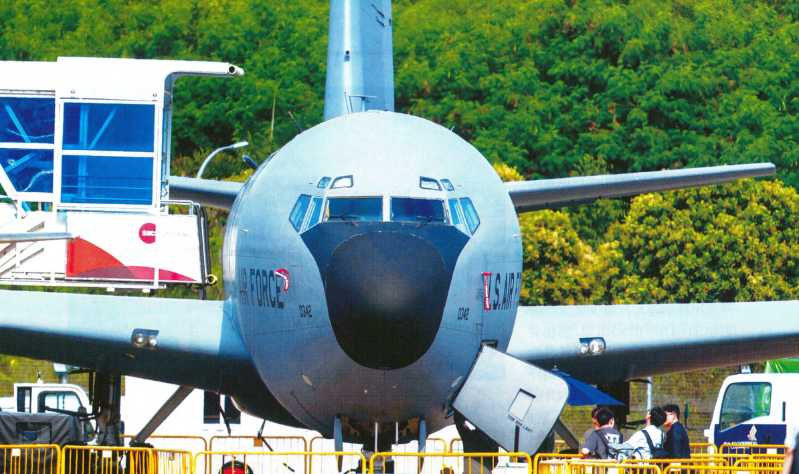
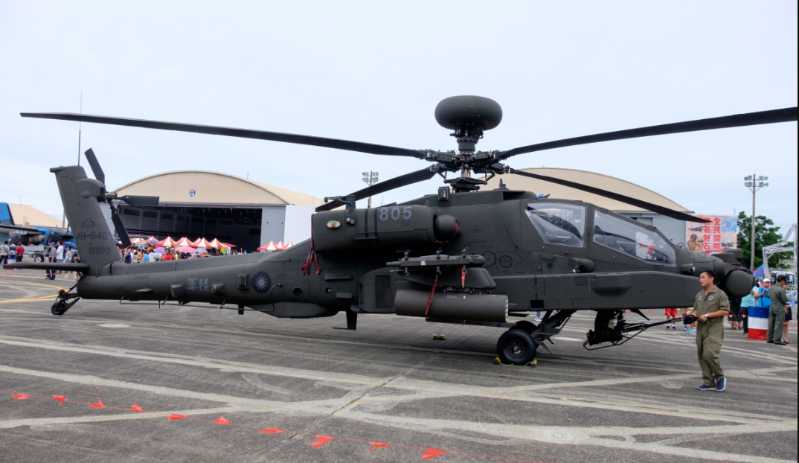
Recently, a video on CCTV’s military column reporting on the Eastern Theater Air Force’s replacement of a mixed reality maintenance system sparked heated discussions. In the video, maintenance personnel wearing a pair of head-mounted displays stood in front of a fighter jet, and could check the aircraft’s pre-flight preparations through virtual operations, and could operate virtual equipment to simulate maintenance and virtual disassembly of the aircraft. A short report revealed a lot of information, reflecting that the Air Force uses technology to empower combat training, organically combining virtual environments with real training, and promoting the transformation of military training from three-dimensional to multi-dimensional, and from virtual parallel to virtual-real linkage.
What is mixed reality technology?
CCTV reported that replacing aircraft engines requires not only perfect quality, but also accurate and reliable speed. A brigade of the Eastern Theater Air Force Aviation Corps put the mixed reality maintenance system into daily work, innovatively using the mixed reality maintenance system to replace traditional card reading and questioning, and realizing virtual disassembly before engine inspection. Empowered by science and technology, accelerating the generation of combat effectiveness!
The mixed reality maintenance system mentioned here is actually a new type of highly simulated interactive virtual maintenance system that combines MR (mixed reality) technology with maintenance. It is mainly used for training and assessment of aircraft maintenance personnel, engine test training, special training and basic training. It is a very advanced application technology.
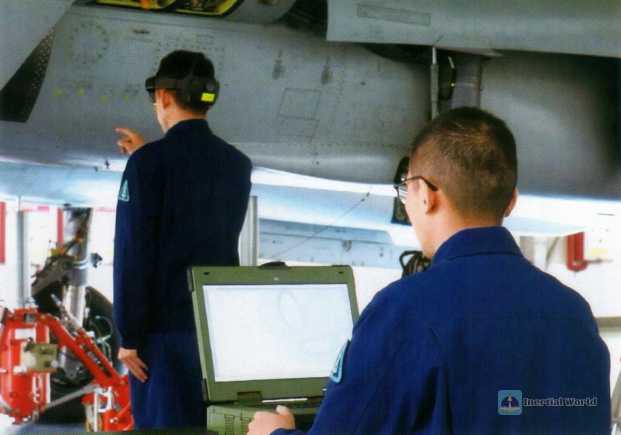

So, what is MR (mixed reality) technology, and how is it different from VR and AR technology?
VR (Virtual Reality) is virtual reality. The biggest feature is that it uses computer simulation to generate a three-dimensional virtual world, providing users with simulations of vision, hearing, touch and other senses, with a full sense of "immersion" and "presence", making users feel like they are in the scene. In this virtual space, users interact with things in the virtual world, and everything you see is computer-generated and fake.
AR (Augmented Reality) is augmented reality. It is a new technology that "seamlessly" integrates real-world information and virtual-world information. It increases users’ perception of the real world through information provided by computer systems, and superimposes computer-generated virtual objects, scenes or system prompts on real scenes, presenting scenes that cannot be realized in the real world, thereby achieving "enhancement" of reality and achieving a sensory experience beyond reality. For example, the currently popular AR navigation is to present intuitive 3D navigation instructions, such as arrows, road signs, routes, etc. in real-time in the real road scene taken, so that users do not need to be distracted by looking at the map, just follow the prompts on the screen.
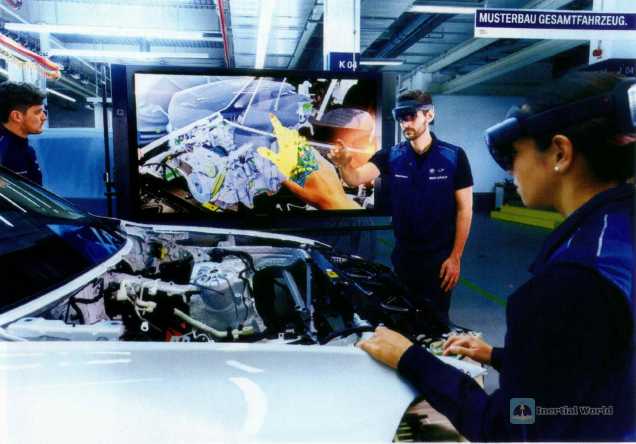

MR (Mixed Reality) is mixed reality. It combines digital information with real-world scenes, allowing users to see both the real world and the images or objects of digital information to produce a new, enhanced reality experience. Sometimes referred to as "augmented mixed reality (AHMR)", the biggest feature is that the virtual world and the real world can interact. MR technology allows the real self to interact with virtual (or physical) objects and scenes at will, achieving the interweaving of virtual and real. Get rid of the limitations of the display and manipulate holographic images with your hands in the air. In comparison, VR puts people in the virtual world to let people experience the sensory stimulation brought by the illusion. AR not only retains the perception of the real world, but also integrates digital information into the real world, allowing users to interact with digital information more naturally. MR is a hybrid technology form developed on the shoulders of VR and AR, which integrates virtual elements with the real world through smart glasses or head-mounted devices. It allows users to interact with virtual objects more intuitively and naturally while being immersed in the scene. For example, pick up a virtual ping-pong ball and then let go. The ping-pong ball will bounce and make a sound when it hits the table. So from the perspective of expression, compared with AR, MR emphasizes the seamless integration and two-way interaction between virtual objects and the real world.

Application of MR technology
Because MR technology allows users to interact between the virtual world and the real world, it has begun to be used in the industrial field, allowing experts to remotely guide technicians, and allowing meeting participants to participate in online meetings with virtual images and interact with each other. In the design industry, the design model can be freed from the limitations of the display, and the holographic image model can be directly manipulated in the air by hand, and it can be enlarged and decomposed in real time, etc., to help designers understand and communicate. Through MR equipment, doctors can interact with virtual models and combine surgical operations with virtual models, such as using mixed reality technology to study patients’ 3D computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images, thereby helping surgeons accurately locate the surgical site.
my country is currently first-class in the research and application of MR technology. As early as 2018, Wuhan Union Orthopedic Hospital successfully implemented the world’s first remote consultation surgery in three places using mixed reality (MR) technology. The entire surgical scene was extremely sci-fi. A team of orthopedic experts from Wuhan, China and Virginia Tech in the United States wore special helmets and consulted with patients far away in Xinjiang Bor People’s Hospital through holographic projection imaging, and then guided the surgeon in Xinjiang Hospital to perform surgery according to the surgical path marked on the lesion projection.
MR aircraft maintenance system
MR technology has the characteristics of presenting virtual scene information in real scenes. In addition to being used in medical surgery, it is also particularly suitable for the field of aviation maintenance. By using MR technology and physical scanning and recognition, the connection between virtual and reality is realized, forming a multimedia interactive system combining vision, hearing and touch, breaking through the constraints of space, time and reality, and projecting a comprehensive, realistic and interactive aircraft model in the real world, thereby building a three-dimensional mixed reality maintenance system.
Users only need to wear a lightweight head-mounted display to observe the three-dimensional model of the aircraft in their field of vision, and can also interact with the model through gestures. When two fingers of the hand touch a part or component, they can freely grab/move any component. When the action instruction is a pinching action, the corresponding object moves with the hand position. When the pinching action is canceled, the corresponding object stops following. Users can freely learn the corresponding maintenance theory knowledge and perform virtual operations.


For the most important aircraft engine on the aircraft, due to the complex internal structure, many parts, high maintenance difficulty, expensive mechanical parts, and the performance of the engine is deeply affected by the maintenance quality, the engine maintenance requires extremely high operating skills of the maintenance personnel. At present, the maintenance of aircraft engines mainly relies on reading paper documents or consulting electronic manuals. The readability is poor and it is not easy to understand and use. Assembly errors are prone to occur during the maintenance process, and there are few opportunities to practice, which is not conducive to the accumulation of maintenance skills and experience.
After using MR technology, the multimedia interaction method of mixed reality technology and the visualization function of three-dimensional models can be used to build a realistic aircraft engine model: combined with holographic images, and through gesture recognition, tactile feedback, physiological calculation and voice interaction technology, the disassembly, size/material design, assembly and operation simulation of engine parts can be realized. It enables ground crew to enjoy an immersive engine disassembly experience from a first-person perspective, participate in the simulation model in the virtual environment, and master the engine maintenance work.
In this CCTV report, the mixed reality maintenance system of the Eastern Theater Air Force uses MR technology. From the report video, we can see that after ground crew members wear MR equipment, they can observe and operate from a "first-person" perspective. They can see the selection interface, virtual tools attached to the aircraft maintenance cover, and virtual wrenches attached to physical parts. Users can perform virtual operations through hand movements to simulate maintenance operations on fighter jets.
Through the mixed reality maintenance system, ground crew members can save training time on real aircraft, conduct training that is difficult to operate on real aircraft in a virtual environment, free them from environmental interference and objective conditions, immerse themselves in the simulation training scene, and receive more comprehensive system training and practical training. Ground crew members can not only learn theoretical knowledge in a completely safe environment, but also conduct simulated cycle tests and more practical operations, complete real troubleshooting tests and collaborative exercises, and thus greatly improve maintenance skills.
In addition, if the mixed reality maintenance system is combined with 5G technology and cloud technology, a multi-person collaborative maintenance training system can be built, thus breaking the limitations of time and space, allowing ground crews in different air force bases to learn and train in the same virtual area, view the structure, system, equipment information and operating principles of the aircraft, and at the same time, when a user operates a passive object, the various changes in its form will be synchronized to the characters in all scenes, training the collaborative operation ability of the ground crew.

Technology empowers military training
Science and technology are the most active and revolutionary factors in military development. Technological development not only gives rise to new means of warfare, but also changes the forms, means and methods of military training. Today, as the form of war is evolving rapidly, the importance of technological factors in building a military training system has risen sharply. In recent years, cutting-edge technologies such as big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence have developed rapidly, and have great application potential in the field of military training.
Facing new situations and new technologies, military training must stand at the forefront of science and technology, explore realistic paths for science and technology to empower training, innovate training models and combat effectiveness generation models, and accelerate the transformation and upgrading of military training. President Xi Jinping stressed that it is necessary to strengthen the consistency between combat and training, adhere to the principle of leading training with combat and promoting combat with training, train according to actual combat requirements, realize the integration of combat and training, promote the integration of virtual and real training, and "build a battlefield outside the battlefield" under certain time and space conditions and relying on a certain support foundation.

The mixed reality maintenance system currently in use in the Air Force is a practical example of science and technology empowering the construction of a combat training environment. By making good use of virtual reality, holographic imaging, mixed reality and other technologies, the "hyper-real" scene can be quickly linked to the training environment. The path of constructing a combat environment is discussed from multiple perspectives, including feasibility, applicability, suitability, and economy. The irreplaceable functional status of real-life training is fully valued, and the virtual environment is organically combined with real-life training to promote the transformation of military training from three-dimensional to multi-dimensional, and from virtual parallel to virtual-real linkage.















