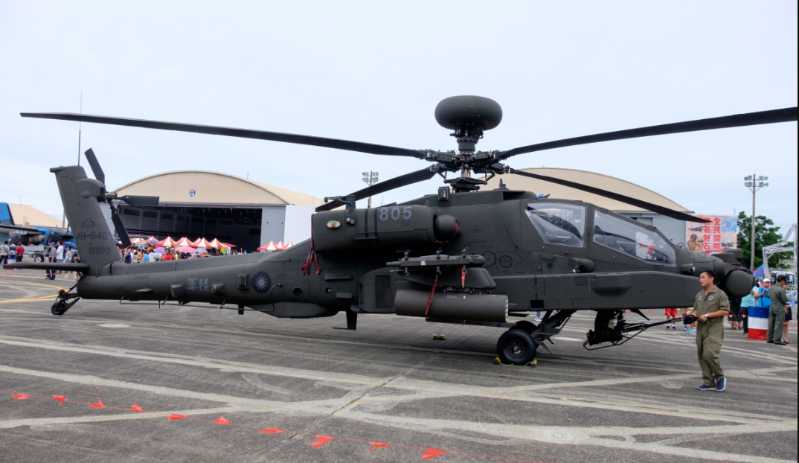
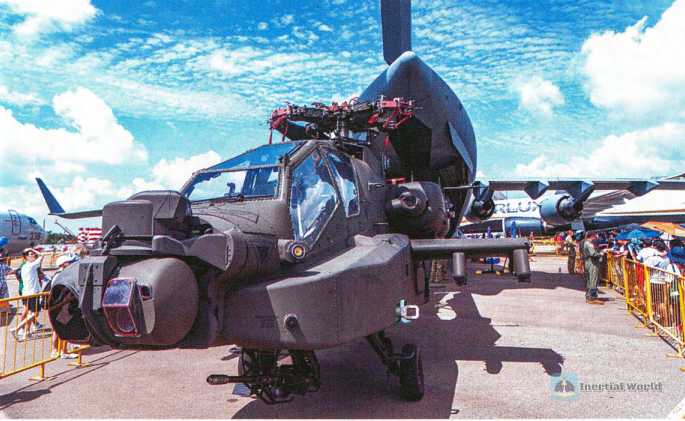
The highlight of the weapons and equipment displayed by Singapore, the host of this air show, is definitely the AH-64D "Longbow Apache" on public display. The "Apache" armed helicopter on public display is majestic and majestic, and the cockpit is in full view, allowing visitors to explore the internal structure of the helicopter. In addition, the ammunition in front of this Apache is all training ammunition (the blue ring mark on the ammunition body indicates that it is a training ammunition, and the real ammunition is yellow ring). The training ammunition has the same appearance and weight as the real ammunition except that it is not loaded with gunpowder, in order to better simulate the aerodynamics of the aircraft in the combat mounting state during flight training.
It can be said that the "Apache" publicly displayed in Singapore this time hints at the impressive strength of the Singaporean troops.

The King of Helicopters
The AH-64 "Apache" attack helicopter is a main attack helicopter designed and manufactured by Boeing for the US Army. It is named after the Native American "Apache". It was developed based on the US Army’s advanced attack helicopter project and is the successor to the AH-1 "Cobra". The project was bid by five companies, Boeing, Bell, Hughes, Lockheed, and Sikorsky; in the end, the US military selected the designs of Bell Helicopter and Hughes Aircraft Company to pass the conceptual design stage and enter the second stage of bidding. Hughes’ concept aircraft was numbered Model-77, military number YAH-64; Bell’s design was Model-409, military number YAH-63, and both prototypes began flight testing in September 1975. After fierce competition, the U.S. Army announced the victory of YAH-64 on December 10, 1976, and gave it the official number of AH-64, becoming the second professional armed helicopter of the U.S. Army after the AH-1 series.
The first mass-produced model of AH-64 is AH-64A. AH-64 is an all-weather two-seat armed attack helicopter. It was officially put into service in 1984 and achieved initial combat capability in July 1986. The aircraft is 17.76 meters long, with a rotor diameter of 14.63 meters, a height of 4.05 meters, an air weight of 5165 kilograms, and a maximum take-off weight of 10433 kilograms. The engine uses two General Electric T-700 turboshaft engines installed on both sides of the rotating shaft. The maximum ceiling is 6400 meters, the flight speed is 365 kilometers per hour, and the combat radius is 480 kilometers.
The aircraft adopts a tandem cockpit layout. This design ensures that the vision of the front and rear pilots is not blocked, which greatly improves the reliability of the driver’s driving. The seating arrangement is that the main pilot is at the back and the co-pilot and gun aimer is at the front. The armor of the driver’s seat can withstand the shooting of the Russian ZSU-23 cannon and can provide protection for the crew when the helicopter crashes. The "Apache" is also equipped with rotor blades with titanium alloy leading edges. The core structure of the rotor blades is that each blade contains five stainless steel arms, which are called "spars", and the spar is surrounded by a fiberglass skeleton. The trailing edge of each blade is wrapped with a solid graphite composite material, and the leading edge is made of titanium alloy. The same as the tolerance of the body, even the rotor can withstand the attack of 12.7mm armor-piercing shells and 23mm high-explosive shells.
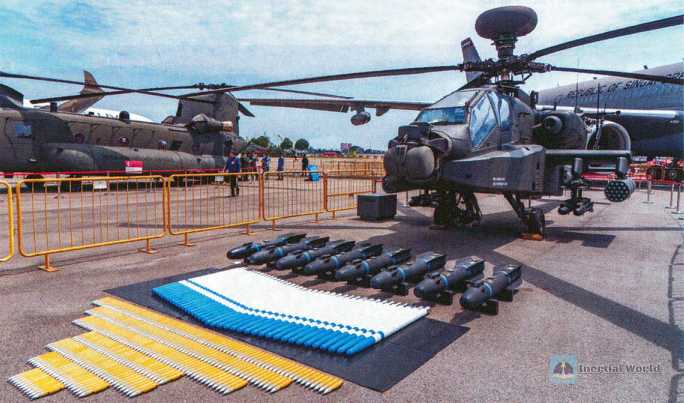

In terms of airborne weapons, the "Apache" is fixedly armed with a 30mm M-203 chain gun installed in the nose. The rate of fire of the M-203 can be adjusted, with a normal rate of fire of 625 rounds per minute and a maximum rate of fire of 1,000 rounds per minute. The muzzle velocity is 808 meters per second, the turret’s rotation range is 110 degrees to the left and right, and the internal ammunition capacity is as high as 1,100 to 1,200 rounds. Its main ammunition type is the M-789 high-explosive armor-piercing dual-purpose anti-personnel projectile (HEDP), which can penetrate the weaker sides and top of light armored vehicles or main battle tanks, and the personnel killing radius is about 5 meters. There is a short wing on each side of the fuselage, and each short wing has two mounting points. Each mounting point can mount an M-261 19-mounted 2.75-inch (70 mm) Sea Serpent-70 rocket launcher (or an M-260 seven-mounted 70 mm rocket launcher), and a set of four-mounted M-299 missile launchers with AGM-114 "Hellfire/Hellfire" anti-tank missiles.
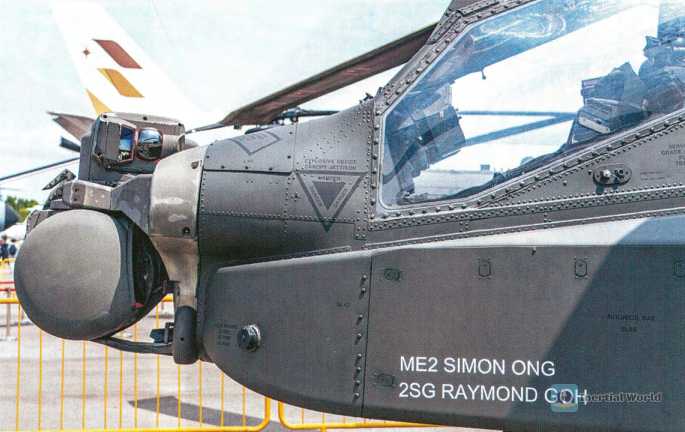
In terms of avionics, the AH-64A had the first-class observation/fire control system at the time. The main observation system was located in the nose and was divided into two parts: the AN/ASQ-170 Target Acquisition Designation System (TADS) and the AN/AAQ-11 Pilot Night Vision System (PNVS).
TADS is divided into five parts: laser rangefinder and calibrator, forward-looking infrared system (FLIR), gunner-specific optical direct sight, daytime TV camera and laser calibrator, all installed in a rotating tower with a dual-axis stabilization system located in the nose, allowing the crew to smoothly aim at the target during intense tactical movements, and the use of FLIR greatly increases the night combat capability of the AH-64A.
PNVS is a FLIR specially designed for night flight, located in an independent rotating tower above the nose, allowing pilots to have clearer external images when flying in dangerous night terrain. The horizontal rotation range of TADS is 120 degrees to the left and right, and the vertical pitch range is -60-+30 degrees; while the horizontal rotation range of PNVS is 90 degrees to the left and right, and the vertical pitch range is -45-+20 degrees. The AH-64A replaced the starlight night vision goggles with FLIR as the main night vision system on board, which was a major innovation at the time. The basic operating principle of traditional starlight night vision goggles is to amplify weak external visible light sources. In environments where external light sources are blocked, such as bad weather and thick smoke, their effectiveness will be greatly reduced. In addition, they cannot penetrate cover. The passive sensing of external infrared signals by FLIR can theoretically overcome this obstacle and even detect enemy targets in bushes and bunkers.
AH-64A became the world’s most powerful and most sophisticated armed helicopter as soon as it was launched. Its observation/fire control system and combat capability are superior to any Russian or other Western armed helicopters in service before the 21st century, and it is still the most powerful armed helicopter in the Western world. At the same time, the "Apache" attack helicopter also participated in several large-scale battles around the 1990s and performed brilliantly.
In December 1989, the United States invaded Panama to participate in the military operation to arrest General Manzil Noriega (code-named "Operation Just Cause". At that time, 11 AH-64A participated in the operation.


When the Gulf War broke out in 1991, the US Army sent a total of 277 AH-64A to the battlefield. With its excellent fire control system and powerful mobile firepower output, it crushed Iraq’s large and useless armored forces like a rotten wood, and almost stole the limelight of the British and American ground firepower output. The performance of the "Apache" in the Gulf War was extremely outstanding. After the war, the report said that it destroyed about 3,700 tanks of the Iraqi Army at the cost of only one, achieving a shocking 1:3,700 loss ratio.
After the "9.11" terrorist attacks, the United States tilted its hatred to the Afghan battlefield, turned its revenge to the Afghan government that had always sheltered the Taliban, and launched a military operation code-named "Enduring Freedom" against Afghanistan in March 2002. The AH-64A helicopter also participated in this anti-terrorism war. However, Afghanistan’s military strength is different from Iraq’s, and its armored strength is weak, so the AH-64A can only be used as air fire support. This piecemeal military operation is not suitable for A The combat characteristics of the H-64A, and the Afghan infantry also developed a simple, low-cost and effective anti-helicopter tactic, which is to fire a large number of cheap RPG shoulder-fired anti-rocket rockets at the AH-64A formation, resulting in the US AH-64 fleet not gaining much advantage.

The famous "Longbow Apache"
And the public display in Singapore this time is the A, known as the "strongest Apache". H-64D "Apache Longbow". Compared with AH-64A, AH-64D is equipped with a more advanced sensor and weapon system, which can perform low-altitude close-range combat attacks, deep precision strikes and armed reconnaissance in all-weather environments.
The biggest upgrade of "Apache Longbow" is the use of A-type helicopter host combined with millimeter-wave fire control radar, radar radio frequency jammer, radar-guided AGM-114 air-to-ground missiles and other cockpit management and digitalization improvements.
Among them, the most The important thing is the origin of the name "Longbow". The AN/APG-78 Longbow millimeter-wave radar system is a coherent Doppler pulse radar with an operating frequency of 35 GHz. It can work in various adverse weather conditions such as sunny days, nights, smoke, fog, dust, rain, snow, and electronic countermeasure environments. The detection range for moving targets is 8 kilometers, and the detection range for fixed targets is 6 kilometers: it can scan the area 55 kilometers in front of the helicopter, and simultaneously display, distinguish and track 128 targets. It can sort 16 threat targets according to priority and attack them within 1 minute.
The "Longbow" radar has low transmission power and adopts low-detectable technologies such as extremely narrow pencil beam main lobe and confidential low intercept rate modulation.
It also uses real beam to measure ground targets, conduct non-cooperative target identification, can penetrate camouflage and leaves to identify fixed targets, and finally display real beam video and synthetic images. It can perform 360-degree continuous scanning in all directions, and can also perform focused scanning on specific sectors. The FCR radar is also a multi-function radar with four working modes: ground target aiming, air target aiming, terrain display and internal testing.
After installing the "Longbow" radar, the technical level and comprehensive combat capability of the "Apache" have been significantly improved, and it has also changed the situation where the AH-64A needs to be accompanied by an OH-58 helicopter or other battlefield reconnaissance equipment to provide target data during combat. After installing the radar, it can search and track targets autonomously. The detected target data can not only be transmitted to other helicopters through data links, but also be linked with the radar-guided AGM-114 "Longbow Hellfire" missile, and use the MMWI radar seeker to detect, capture and track the targeted threat targets.


AGM-114 "Longbow Hellfire" is a precision strike missile guided by millimeter-wave radar. It is also the world’s first helicopter-borne, fire-and-forget heavy long-range anti-tank/anti-helicopter missile. The missile has a range of 0.5-10 kilometers, and the warhead can use dual-purpose grenades or two-stage tandem shaped-charge projectiles as needed. During combat, the onboard fire control radar searches for the target, and after determining the target, the missile is launched. The millimeter-wave seeker on the missile searches, locks on the target, and attacks the target. Moreover, the millimeter-wave seeker can also be used as a proximity fuze to detonate the warhead and destroy the target at the right time. This guidance method enables the missile to truly have the ability of "fire and forget", and can effectively avoid interference from rain, snow, fog, smoke and other barriers on the battlefield (which cannot be done by laser semi-active guidance), greatly improving the attack capability and survivability of the carrier aircraft.
Relying on its excellent platform, powerful firepower, and advanced integrated fire control system, the AH-64D once won the title of the world’s most powerful armed helicopter and was purchased by many countries, including these 20 in Singapore.
Currently, the US military’s A H-64D has developed to Block I and has been renamed A H-64E "Guardian Apache". The main improvement of the A H-64E is that it has greatly improved the connection capability of digital information, is compatible with the Joint Tactical Intelligence Distribution System, and has been replaced with a higher-output T700-GE-701D engine. In addition, the new model also has a remote-controlled unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), complete instrument flight rules, and an improved landing gear. The new rotor made of composite materials has improved the new model’s cruising airspeed, climb rate, and payload capacity.
Related reading
- 国产大飞机海外首秀:中国商飞C919和ARJ21飞行展示
- Domestic large aircraft overseas debut: COMAC C919 and ARJ21 flight demonstration
- 从美军B-52H战略轰炸机双机通场新加坡航展说起
- 近距离观察F-35A隐形战斗机
- 近观新加坡F-15SG战斗机
- 我进入了F-16D的座舱
- 新加坡航展上的萨博“鹰狮”JAS-39战斗机
- 我当上了苏-30的飞行员--苏-30MKM战机前的超强体验
- 中国的“老朋友”--来自冲绳的P-8A反潜巡逻机
- 又见C-17运输机
- 首次亮相新加坡航展的直-10ME
- 静态展示的CH-47F“支努干”重型运输直升机
- KC-135下的漫步,不得不说的硬管加油装置
- 细看新加坡“紫菀”-30防空导弹
- 先进机型齐亮相---新加坡航展上的中航展台
- 混动装甲战车--新加坡“特雷克斯s5”轮式装甲车管窥
- 2024年新加坡航空展室内展台参观记