In the ground-strike arsenal available to Russian combat aircraft, the family of precision-guided bombs is an important part. Thanks to continuous testing and improvement in actual combat, the Russian precision-guided bombs have also developed multiple series, with multiple guidance methods and multiple warheads, which greatly enhances the ground-strike capability of Russian combat aircraft. This article will take stock of this large family with a hundred flowers blooming.
Origin
In terms of precision-guided weapons, the Soviet Union started relatively late. After World War II, the former Soviet Union developed the UB-2F "Seagull" guided bomb based on the "Fritz X" radio-guided bomb used by Germany during the war. The bomb has an X-shaped delta wing in the middle of the bomb body, an H-shaped tail and a light-emitting device at the tail. It is remotely controlled by the bombardier on the carrier aircraft to fly to the target. The Il-28-131 can be mounted on the belly of the aircraft. A small antenna fairing with a missile radio remote control system is installed under the nose. About 30 aircraft were manufactured in 1956, but they were soon retired. Later, the UB-5000 bomb was developed, but it was not mass-produced. The United States used the first generation of precision-guided bombs to attack important targets in Vietnam during the Vietnam War, which shocked the Soviets. The Soviets quickly absorbed the American design concept and developed their own KAB precision-guided bomb family.
KAB guided bomb family
Starting in 1972, Nikolay Privalov, a designer of the "Region" joint enterprise, led a design team and chose the 500 kg FAB500 low-drag bomb as a breakthrough point, developed the KAB-500L semi-active laser-guided bomb, and put it into mass production in 1975. Later in 1980, they chose the old FAB-1500 high-drag bomb and developed the KAB-1500L semi-active laser-guided bomb. Under the leadership of Boris Meltzalov, by replacing different guidance systems and different warheads, a variety of practical models of two weights were formed, namely the KAB-500 series and the KAB-1500 series.
The so-called KAB is the abbreviation of the Russian corrected aerial bomb. Its naming rule is to add the bomb weight after KAB, and then indicate the guidance method. L is laser semi-active guidance, LG is enhanced laser semi-active guidance, Kr is TV guidance, S is satellite guidance, and TK is data link optoelectronic guidance. The warhead type is marked at the end of the name. F stands for high explosive, Pr stands for earth drilling, OD stands for thermobaric warhead, K stands for cluster warhead, and U stands for training. The most important thing is the change in the guidance part.
KAB laser-guided bombs
KAB laser-guided bombs all use the weathervane 27N/27N1 laser semi-active seeker. The characteristic is that there is a wind-fixing stabilizing ring behind the cylindrical seeker, which is connected to the control cabin through a universal joint. When the bomb is dropped, the stabilizing ring will deflect the seeker under the action of the airflow, and always aim at the target stably. The angle formed between the seeker and the bomb body is the attack angle of the bomb during flight. The seeker works at 1.06 microns, and the capture distance for laser signals is 5-7 kilometers, with a field of view of 12.5 degrees (some say 25 degrees). The bomb adopts a canard layout, with 4 fixed stabilizer wings installed on the head, and 4 rectangular tail wings and mechanical relay-type servos at the rear to control the rudder surface. The pitch control efficiency is high. There will be infrared signals at the tail of the bomb to facilitate the tracking of the optoelectronic pod. The KAB-1500 tail wing is also designed with a deployment mechanism.
Precision-guided bombs using this type of seeker include KAB-500L-Pr concrete-penetrating bomb, KAB-500L-F high-explosive bomb, KAB-500L-OD thermobaric bomb, and KAB-500L-K submunition bomb. KAB-1500L-Pr concrete-penetrating bomb, KAB-1500L-F high-explosive bomb, and KAB-1500L-OD thermobaric bomb. KAB-500L weighs 525 kg, is 3.5 meters long, has a diameter of 380 mm, a warhead of 450 kg, a maximum throw distance of 9 kilometers, and a strike accuracy of 7-10 meters. KAB-1500L has a total length of 4.6 meters, a bomb diameter of 580 mm, a maximum wingspan of 1.3 meters, a total weight of 1560 kg, a warhead of 1180 kg, a strike accuracy of 7-10 meters, and a maximum throw distance of 15 kilometers. In September 2005, Russia also demonstrated the prototype of the KAB-250L laser-guided bomb, but it was not mass-produced.
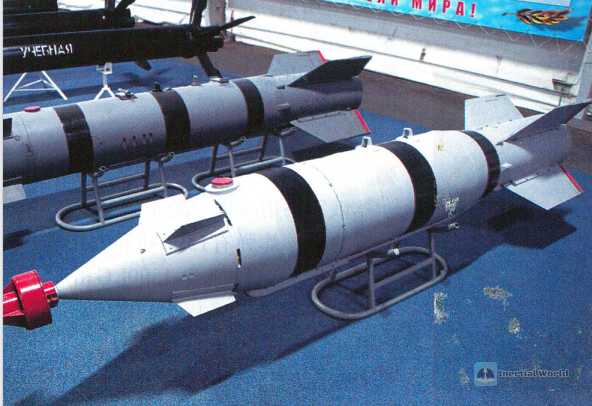
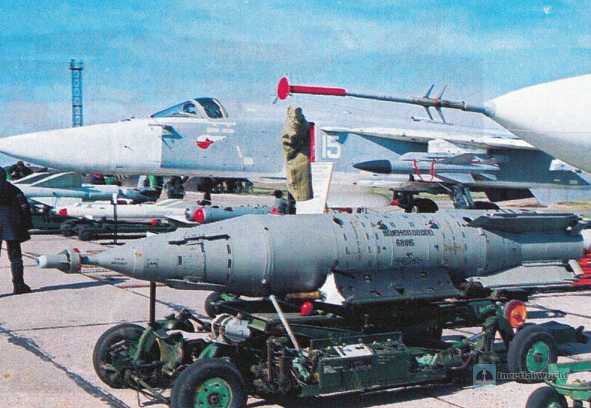
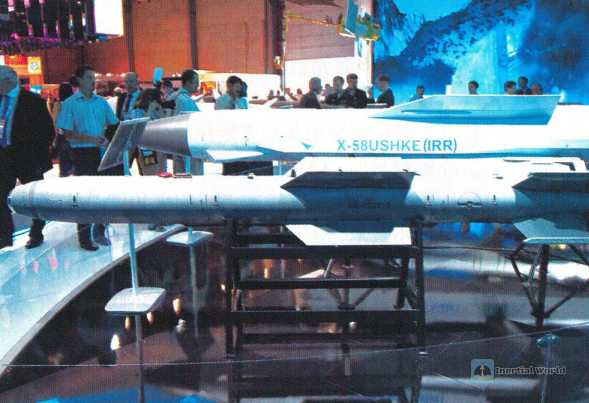






2. KAB improved laser-guided bomb
Russian military uses improved laser-guided seekers in guided bombs of 1,500 tons and 250 tons, including KAB-1500LG and KAB-250LG. KAB-1500LG adopts the second-generation laser semi-active proportional seeker, which has strong anti-interference ability and wide field of view. It can strike low-speed moving ground targets and can attack multiple targets at the same time. It has strong all-weather capability. The seeker adopts a spherical transparent fairing with a metal mesh structure, a three-degree-of-freedom laser gyro stabilized platform, laser elements and processing components, etc. It adopts proportional guidance law and is controlled by an autopilot and four rudder transmission devices.
The KAB-1500LG laser-guided bomb weighs 1,525 kilograms, the warhead weighs 1,170 kilograms, including 440 kilograms of explosives, the bomb diameter is 0.58 meters, the length is 4.28 meters, the wingspan is 1.3 meters when unfolded, and 0.85 meters when retracted. The maximum throwing height is 8 kilometers and the minimum throwing height is 1 kilometer. The maximum throwing speed is 1,100 kilometers per hour, the minimum throwing speed is 550 kilometers per hour, and the hit accuracy is 4-7 meters. According to the different warheads used, KAB-1500LG includes KAB-1500LG-FE with high explosive warhead, KAB-1500LG-Pr-E with 1120kg charge and 210kg earth-penetrating warhead, and KAB1500LG-OD-E with 1170kg charge and 650kg thermobaric warhead.
At the 2011 Moscow Air Show, KTRV Joint Stock Company exhibited the KAB-250LG glide-guided bomb developed by SNPP Regional Joint Stock Company. This bomb has a missile-like shape, with a small aspect ratio wing in the middle and four tail fins with rudders at the tail. It is said that it adopts a modular design and can be switched to laser guidance and satellite guidance, but there is no real satellite-guided missile so far. The KAB-250LG is 3.2 meters long and weighs 256 kilograms. It carries a 165-kilogram high-explosive fragmentation warhead, contains 90.7 kilograms of explosives, and is equipped with a trigger fuse with three delay modes. The drop height is 1,000-10,000 meters, the aircraft speed is 200-350 meters/second during drop, and the strike accuracy may be around 3 meters. This small guided bomb is likely to be used in conjunction with the Su-57’s bomb bay.

3. KAB TV-guided bomb
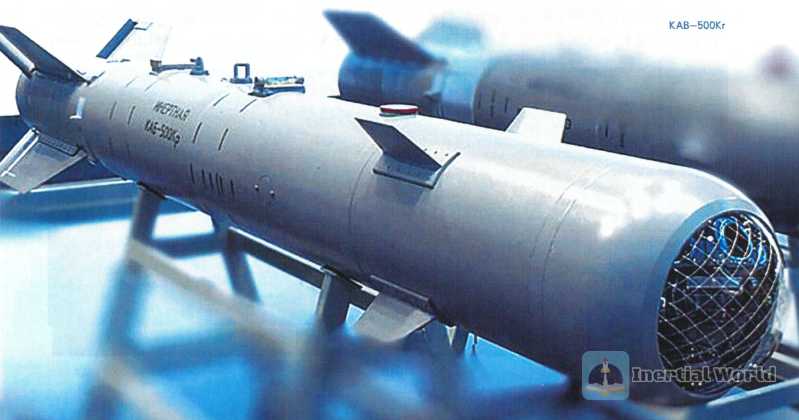
KAB TV-guided bombs all use the TUSS-2 white light TV self-seeking seeker, a spherical transparent fairing with a metal mesh structure, a three-degree-of-freedom gyro-stabilized platform, optical elements and processing components. The swing angle of its gyro stabilizer is ±45°, the heading is ±40°, the pitch is +35°~-57°, and the automatic tracking angular velocity is 7 degrees/second. The optical element has a field of view of 3.2° and has anti-radio electronic interference function. Even if 40% of the objective lens field of view is covered, the seeker can still perform target intelligence processing and correction. Due to the poor resolution of the seeker, it has to be equipped with an optoelectronic scene matching device to attack low-resolution targets through the contrast of nearby terrain features or objects. It also has no infrared function and can only be used during the day and without battlefield cover. It does not have all-weather combat capabilities. Both weight ammunition are modified based on the laser-guided type.
The TV-guided seekers include KAB-500KrPr concrete penetrators, KAB-500Kr-F high-explosive bombs, KAB-500Kr-0D thermobaric bombs, KAB-500Kr-K submunitions, KAB-1500Kr-F high-explosive bombs, KAB-1500Kr-Pr concrete penetrators, and KAB-1500Kr-0D thermobaric bombs. The KAB-500Kr-F high-explosive TV-guided missile has a total weight of 520 kg, a warhead weight of 380 kg, and an explosive weight of 100 kg. The bomb is 3.05 meters long, 0.35 meters in diameter, with a tail wingspan of 0.75 meters, a drop height of 0.5-5 kilometers, a drop speed of 550-1100 kilometers per hour, and a strike accuracy of 4-7 meters. The KAB-1500Kr TV-guided bomb has a total weight of 1525 kg, a warhead of 1100 kg, including 440 kg of warhead, 210 kg of explosives, a bomb diameter of 0.58 meters, a length of 4.63 meters, a wingspan of 1.3 meters, a maximum drop height of 8 kilometers, and a minimum drop height of 1000 meters. The maximum drop speed is 1100 kilometers per hour, the minimum drop speed is 550 kilometers per hour, and the strike accuracy is 4-7 meters. In order to train the aiming of these two types of bombs, a KAB-500Kr-U training pod was specially developed. It weighs 85 kilograms, is 1.83 meters long and has a diameter of 0.35 meters. Later, in conjunction with the APK-9 data link pod, it can have the ability to temporarily indicate targets and become the KAB-1500TK



4. KAB satellite-guided bomb
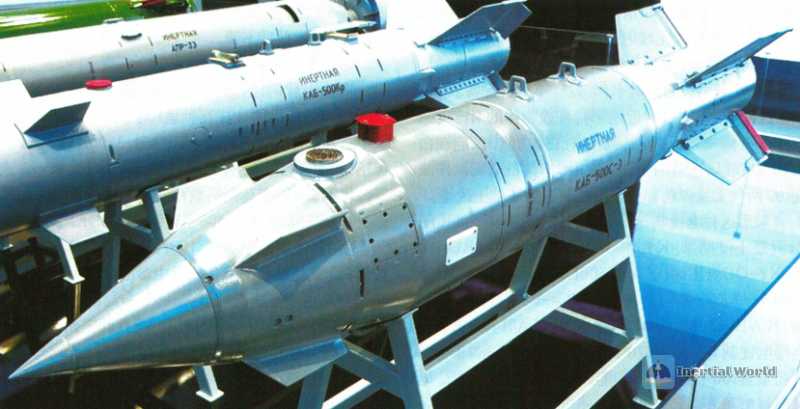
Russia’s satellite-guided guided bomb is the KAB-500S, which is also developed on the basis of the KAB-500L, but has a special pointed shape and is equipped with an inertial navigation + 24-channel PSN-2001 receiver. It can accept Glonass or Navstar satellite signal guidance and has the ability to automatically switch from one system to another. The target position can be pre-set or set before the launch. The KAB-500S satellite-guided high-explosive bomb weighs 560 kg, the warhead weighs 460 kg, the explosives are 195 kg, the length is 3 meters, the diameter is 0.4 meters, the tail wingspan is 0.75 meters, the drop height is 0.5-5 kilometers, the drop speed is 550-1100 kilometers per hour, the strike accuracy is 7-12 meters, and it can be fired and forgotten
UPAB guided glide bomb
The Soviet-era design bureau did not develop glide guided bombs. It was not until September 2005 that the Russian side displayed the UPAB-1500Kr prototype bomb at the open day event of the Valery Chkalov State Flight Test Center, but there was no news afterwards. Until 2019, the Russian Tactical Missile Weapons Company (KTRV) launched two types of satellite-guided munitions for standoff delivery at the Moscow Air Show, including the 500 kg K08BE/UPAB-500B and the 1.5 ton K029B/UPAB-1500B satellite-guided glide bombs, which have already participated in the Russian-Ukrainian war. These two types of glide-guided bombs use a special circular warhead, an X-layout front wing and a rear tail rudder design. The K029B also has a foldable delta wing surface, which is why it has a long range effect. They also use inertial navigation + Glonass and GPS civil code satellite guidance mode.
K08BE/UPAB-500B glide bomb is 2.84 meters long, 0.355 meters in diameter, weighs 505 kg, has a 390 kg high explosive warhead, equipped with a contact fuze with three delay modes, has a service life of about 15 years, can be thrown from an altitude of 14 kilometers, has a range of 40 kilometers, and a CEP of no more than 10 meters. K029BE/UPAB-1500B is 5.05 meters long, 0.4 meters in diameter, weighs 1525 kg, carries a 1010 kg concrete-penetrating high explosive warhead, and is equipped with a contact fuze with three delay modes. The bomb can be thrown from an altitude of 15 kilometers, has a range of 50 kilometers, and a circular error (CEP) of up to 10 meters.
Thunderbolt E2 glide guided bomb
The Thunderbolt-E2 glide guided bomb is developed from the Thunderbolt-E1 cruise missile. It adopts a common cylindrical bomb body with a pointed cone, a large aspect ratio folding swept wing and tail rudder design, and is mounted on an AKU-58U ejection rack. It is 4.2 meters long, 0.31 meters in diameter, 1.9 meters in wingspan, and weighs 598 kilograms. The Thunderbolt-E2 mainly removes the engine and replaces it with a 165-kilogram 9-Zh2-7759 MBCHd additional warhead module, and then cooperates with a 315-kilogram 9-Zh1-7759 high-explosive fragmentation warhead and trigger fuse, focusing on high power. The glide bomb is equipped with an inertial measurement unit and a GPS/Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS) receiver for guidance, and the strike accuracy is at the meter level. The missile is launched at an altitude of 500-12,000 meters, at a launch speed of 140-445 meters per second, and has a range of 60-65 kilometers.
PBK-500U Drel glide guided submunition
PBK-500U Drel (Drill) gliding guided submunition is developed by the Russian Basalt State Research and Production Corporation (Bazalt). It is mainly used to attack armored vehicles, ground radar stations and missile system control centers. It also adopts a design that reduces the detection capability of enemy radar systems. As early as the mid-1990s, Basalt experts began research on a new type of gliding submunition PBK-500U to improve the combat efficiency and combat readiness of the Air Force. However, the development progress has been delayed by the country’s difficult economic situation, and it was finally exhibited to the public for the first time in 2008. The PBK-500U Drel glide-guided cluster bomb was first exhibited at the 2016 Military Forum, and the first national test began in 2018. As a result, the test completion date was delayed twice, and the performance was not up to standard. Therefore, it was not until January 12, 2024 that the Russian State Technology Group (Rostec) announced that it was ready to start mass production of the PBK-500UDrel glide-guided cluster bomb.
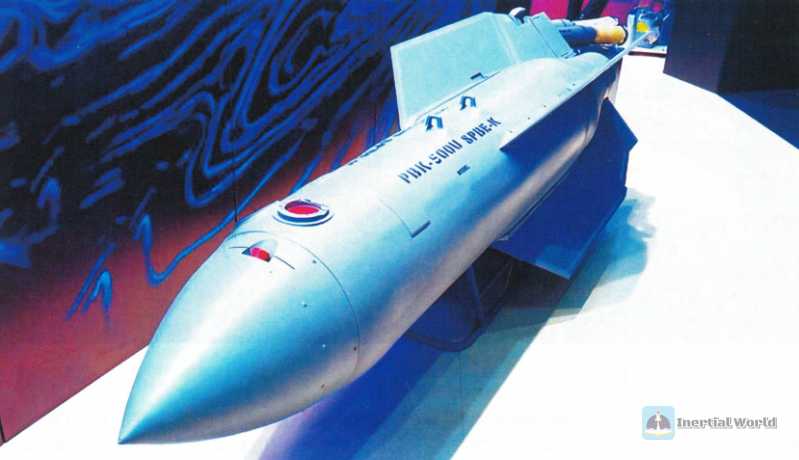

PKB-500U Drel glide-guided cluster bomb weighs 540 kilograms, is 3.1 meters long, and has a diameter of 450 mm. The bomb is released at a height of 100 meters to 14 kilometers, with a flight speed of 700~1100 kilometers per hour and a range of about 50 kilometers. This bomb has a very peculiar wing design. First, its cylindrical bomb body is contracted near the tail, and the transition section is very long, so its wings and rudders are divided into three sections. The main bomb wing is a swept trapezoid, and the auxiliary bomb wing is connected to the main bomb wing. The upper two are equipped with GLONASS receiver antennas, and the rear is 4 control rudders, so a larger rudder is formed to facilitate gliding. According to the Russian side, it also has a stealth effect and is coated with stealth paint. The PBK-500U Drel adopts an inertial navigation + GLONASS guidance system, with a strike accuracy within 10 meters. The target data can be bound on the ground or before the fighter is launched, and it can be dropped at a 30-degree angle relative to the target.
PBK-500U cluster bombs adopt a modular design and can use a variety of charges, including explosive and fragmentation warheads, anti-concrete warheads, incendiary warheads, and anti-tank warheads. The PKB-500U Drel gliding guided bomb is equipped with 15 SPBE-K anti-tank terminal-sensitive bombs. SPBE means self-aiming combat element. This terminal-sensitive bomb is 0.28 meters long, 0.255 meters high, 0.186 meters high, and weighs 14.9 kilograms. It is structured as an upper parachute cabin, which contains auxiliary parachutes and main parachutes of different sizes, and is controlled by commands issued by an electrical system using a burster and a connecting rod mechanism. The lower part is a self-forged fragmentation warhead, about two-thirds of which is occupied by shaped charges and funnel-shaped charge caps, carrying 4.5 kilograms of explosives, which can penetrate 70 mm/30° homogeneous armor. The side is a command cabin and folded stabilizing wings. The command cabin is equipped with a dual-band (3-5 microns and 8-14 microns) infrared seeker and millimeter-wave radar, and a compact radio altimeter.
After the terminal-sensitive bomb is released from the bomb body, the auxiliary parachute is first opened to slow down. After reaching an altitude of 170 meters, the command unit equipped with a radio altimeter issues a command to discard the auxiliary parachute and deploy the main parachute, reduce the descent speed to 15-17 meters per second, and deploy the side angled bomb wings to rotate the bomb body at an angle of 30° to the vertical line and a speed of 6-8 revolutions per second. It scans for 6-9 seconds and gradually searches a circular area with a radius of about 90-100 meters in a spiral shape. When the unique thermal radiation or radar data of the armored vehicle is detected, the command cabin will issue a command to detonate the warhead to destroy the target, and can also identify the enemy based on the radar data. A key safety feature of the DERL bomb is its integrated self-destruction device. If the bomb does not hit the intended target, the self-destruction program is set to minimize the risk of collateral damage.
UMPK guidance kit modified glide bomb
The various precision-guided bombs introduced above are comparable to American products in terms of strike accuracy, but there is a big problem, that is, they are special bombs for special purposes, and only new bombs can be manufactured. The production quantity is small, so the price is expensive, and the Russian military’s glide guided bombs matured very late. Western countries can use MK series bombs to directly install precision guidance kits and glide kits to transform them into JDAM and JDAM-ER, and the transformation is particularly easy. Armorers can directly transform them at the airport, and they are convenient to use. This is something that the old Russian missiles cannot do.
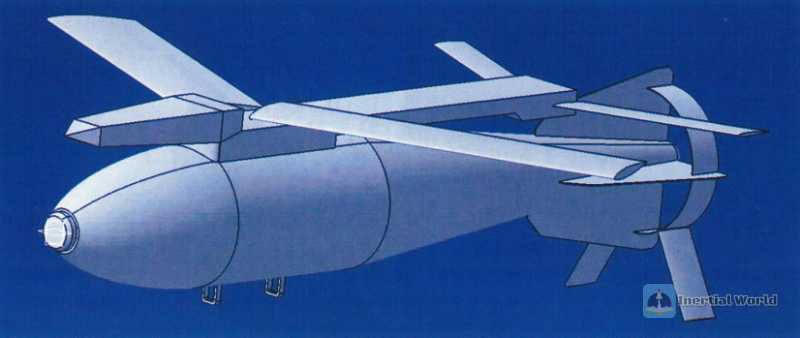
The Russian army also has a large inventory of bombs, including high-drag and low-drag bombs. High-drag bombs are designed to be mounted in the bomb bay of bombers. They have a short and thick appearance, a blunt and even flat head, a small aspect ratio, a large drag coefficient, a ballistic drag ring, and a stabilizer at the tail. Low-drag bombs are designed for external use on fighters, and the shape of the bomb body is relatively slender and streamlined. They use foldable metal cross tails and can be equipped with deceleration parachutes. However, whether it is the FAB-M46, M54 or M62 bombs of the Russian army, the tails of all bombs are directly welded, and they cannot be fixed with screws like the MK series bombs. As long as the tail is replaced, it can be transformed into a guided bomb. On the other hand, the special circular tail of the FAB series also means that if you want to change it, the entire aerodynamic shape will change, and it is difficult to directly replace the tail. The development of Russian military gliding bombs is lagging behind, so the Russian Aerospace Forces’ Su-25, Su-24, Su-34, etc. used for ground attacks either have to launch expensive missiles or have to take the risk of penetrating into the kill zone of Ukrainian air defense missiles at low altitudes to drop bombs in order to achieve precise strikes, resulting in heavy losses.
In 2002, Russia’s Bazat company first displayed four MPK modules for the transformation of the FAB-500M-62 bomb at the Farnborough Air Show in the UK. The basic model only has 1.98-meter wings and no guidance components, and the range of 50-100 meters can reach 6-8 kilometers. The improved model is equipped with a simple inertial navigation system (INS), and the range of 50-100 meters can reach 12-15 kilometers, with improved accuracy. The guided model is equipped with a satellite navigation receiver, and the strike accuracy reaches 0.9 meters from a high-altitude drop distance of 40 to 59 kilometers. The extended-range model will be equipped with a pulse jet engine to extend the range to 80-100 kilometers. But the project has never been put into production
The change occurred in 2023. On January 4, 2023, the Russian Telegram channel released a photo showing a FAB-500M-62 bomb with a UMPK guidance kit mounted on a Su-34, and then the Russian army used bombs with this kit in large quantities to attack Ukrainian targets. The UMPK guidance kit uses a very clever way to bypass the appearance restrictions of the FAB-500M-62 low-drag bomb. The idea can be simply described as hanging a bomb under a small plane. The front of this kit is a four-sided pyramid structure, and the rear is a rectangular structure extending to the tail of the bomb. The entire kit is fixed by two steel bar fixing rings at the front and a fixing ring at the tail of the bomb. Two folded straight wings are installed, which are slightly swept back when unfolded. The tail of the kit is two full-moving horizontal tails to control its pitch, roll and yaw, as well as two inclined vertical tails fixed on the annular tail. The entire production is very rough, with thick welds, and since the structure of the bomb body has not been changed, the price will be quite cheap and it is also very convenient to modify. Because the UMPK guidance kit is easy to modify, and even the bomb body does not need to be modified at all, it has been installed on the FAB-250-M62 low-drag bomb RBK500 submunition.
The core of the UMPK guidance kit is the planning and correction module (IPC) developed by GNPPBazalt. This module is installed in an aluminum box, and inside it is a circuit board with a data interface. It is mainly used for flight control and drives two tail full-moving elevators to control the flight status of the missile. The core of the planning and correction module (IPC) is the Kmeta-M satellite navigation receiver antenna developed by Moscow Vniirt Progress Company. It has 4 CGGP.18.4.C.02 GPSGLONASS/GALILEO dual-frequency patch antennas from Ireland Taoglas. This series of antennas increases the anti-interference capability by 40-50 decibels and covers all operating frequency bands of the GPS/GLONASS system from 1575MHz to 1610MHz, which is equivalent to reducing the interference range imposed by the enemy by 100-300 times, that is, reducing it by 100-300 decibels. The range of this guided bomb is 40-60 kilometers, depending on the flight mode and speed of the carrier aircraft, and its strike accuracy is about 8 to 15 meters.
But this guidance kit cannot solve the problem of the transformation of a large number of Russian high-altitude bombs. In early September 2023, the Russian military’s telegram channel reported that the Russian military used a modified FAB-1500-M54 glide bomb on the battlefield for the first time. The FAB-1500-M54 is an unguided high-explosive aerial bomb designed in 1954, weighing 1,550 kg, of which 675 kg is explosives. It can reach a speed of 1,200 km/h when dropped from an altitude of 16,000 meters. Once it explodes, it will leave a crater 20-25 meters wide and 6 meters deep. The killing distance for personnel is within 70 meters, severe damage, 140-150 meters, moderate damage, and 300-350 meters.
On January 12, 2024, during a demonstration at the Defense Industrial Complex of the Tactical Missile Equipment Company in the Moscow Region, a delegation led by Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu unveiled the FAB-1500-M54 glide guided bomb. This bomb is actually a combination of a 1.5-ton FAB-1500 heavy high-drag bomb and a UMPK glide guidance kit, marking that the Russians have explored a successful way to transform old high-drag bombs.
While the new UMPK guidance kit has been enlarged in appearance, there are four major changes to adapt to the FAB-1500M-54 transformation. First, the other two inclined vertical tails on the tail ring are cancelled, and then the fairing at the head of the kit is staggered with the kit, and the rudder at the tail of the kit has become a tilted design. The biggest change is that the oval body fairing is directly installed on the head of the bomb, which perfectly solves the problem of increasing the range of high-drag bombs. In contrast, the ODAB-1500 thermobaric bomb still uses a kit similar to the FAB-250-M62. After all, it is a configuration similar to a low-drag bomb. Its specific data is unknown, but it should be no different from the 500 kg class.

Conclusion
From now on, the Russian army is still adhering to the two-legged research and development route. On the one hand, it continues the original special bomb special route, continues to develop better precision-guided bombs and glide bombs, and actively expands production to meet the needs of war. On the other hand, it conveniently utilizes its huge inventory of old bombs through different levels of UMPK glide guidance kits to quickly transform simple glide guided bombs, which are more efficient and cheaper. Compared with the U.S. military’s modification of removing the tail of the bomb and replacing the guidance kit, the Russian army has obviously taken a more convenient path of glide guided bomb modification with less modification to the bomb body, thus adding a heavy weight to the enhancement of the survivability and strike capability of Russian aircraft. However, compared with Western bombs that gradually adopt composite guidance mode, Russian guided bombs still focus on single mode, which may be worse in anti-interference. In addition, Russian laser-guided bombs need to cooperate with the Petrel-24 system on the Su-24M and the retractable Platan system on the Su-34 for laser irradiation, but lack advanced optoelectronic pods, so the irradiation range will be limited. The Russians still need to continue to work hard on research and development!

















