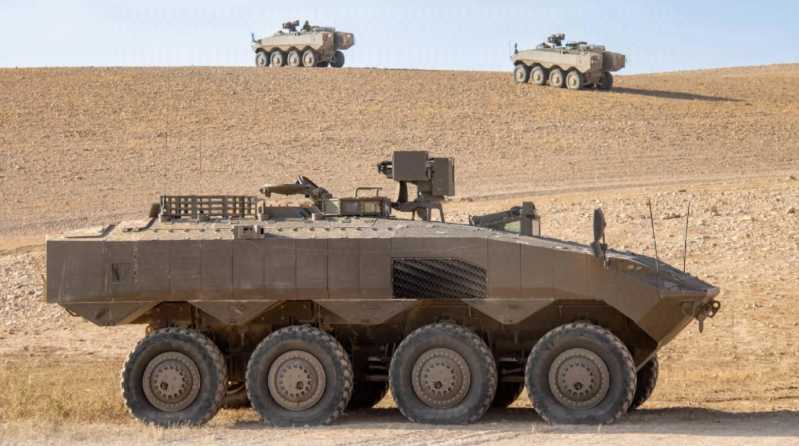
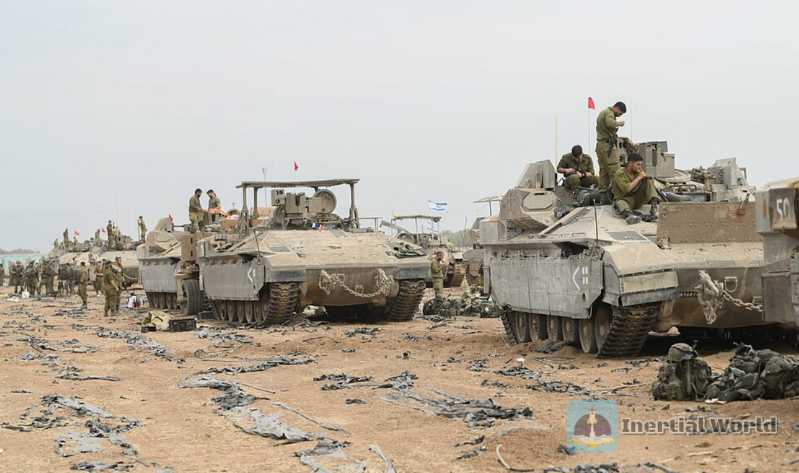
Recently, the Nahal Infantry Brigade of the Israel Defense Forces received the first "Eitan" 8x8 wheeled armored personnel carrier, which is considered to mark a key step forward in the modernization of Israel’s ground forces. On May 28, 2023, the Israeli Ministry of Defense also released a video on Twitter, announcing this important milestone, "In a major development of Israel’s military capabilities, the Nahal Infantry Brigade of the Israel Defense Forces received their first batch of highly anticipated "Eitan" 8x8 armored personnel carriers." "Eitan" was developed by Oshkosh Defense in the United States according to the needs of the Israel Defense Forces. At present, the Israel Defense Forces has ordered hundreds of them, worth more than 100 million US dollars, mainly to gradually replace the tracked M113 armored personnel carriers. Considering the considerable scale of M113 armored personnel carriers retained by the Israel Defense Forces, such a large-scale replacement largely means a kind of vane-like change.
Background
Due to the unique armored culture, the Israel Defense Forces have never equipped any infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs), and various types of armored personnel carriers (APCs) have always played the leading role. For example, the Israel Defense Forces once used the Soviet tanks captured in the Middle East wars to modify hundreds of "Achzarit" heavy personnel carriers. In the same way, the Israel Defense Forces also modified some obsolete "Centurion"/"Shot" and M48 medium tanks into so-called "assault engineer combat vehicles." Of course, the above vehicles are largely waste-recycling and cannot fully meet the needs, so the Israel Defense Forces are also equipped with certain high-end goods, that is, the heavy armored personnel carrier derived from the "Merkava" main battle tank-"Tigress". However, the cost of "Tigress" is very high, which conflicts with the pragmatic style of the Israel Defense Forces. The Israel Defense Forces actually only purchased a very limited number of "Tigresses", and it is generally believed that the number does not exceed 170.

In fact, the US-made M113 armored personnel carrier is the main battlefield mobile tool in the IDF mechanized infantry units. The M113 is famous for being the first mass-produced aluminum-body armored vehicle, with up to 40% of its parts made of aluminum alloy. Although lighter than similar armored vehicles, the aluminum armor developed by Kaiser can still protect the crew and passengers from 7.62mm bullets and shell fragments. The 13-ton M113 is also designed as a multi-purpose armored vehicle that can not only transport soldiers to the front line, but also transport engineers, medical personnel, and mortars and gun crews. It has developed about 40 derivative models, including air defense, artillery reconnaissance and other purposes. The basic M113 has a crew of two, but can accommodate up to 15 soldiers, making it a real "battlefield taxi." The first batch of M113 mass-produced models were equipped with a 209-horsepower Chrysler gasoline engine. Starting from the M113A1, it was replaced with a 275-horsepower 6V53T six-cylinder diesel engine from GMC Detroit Diesel Company. It uses a three-speed automatic transmission and a steering differential, with a maximum speed of 66 kilometers per hour and a cruising range of 483 kilometers. In addition to its light weight and air transport, the M113 also has appropriate amphibious performance and can float at a speed of 5 kilometers per hour by paddling with tracks. When floating, the rubber skirts on both sides of the body can actually play a role in controlling the water flow on the upper part of the track. During the Vietnam War, the M113 was widely used. The D Company of the 16th Armored Battalion of the 173rd Airborne Brigade first used this armored vehicle. This was the first US Army armored unit deployed to Southeast Asia. Facts have shown that this was the first actual combat application of mechanized infantry. Through actual combat, the M113 proved that it could perform tasks such as forced reconnaissance (RIF), search and destroy, and even played an important role in large-scale offensives.
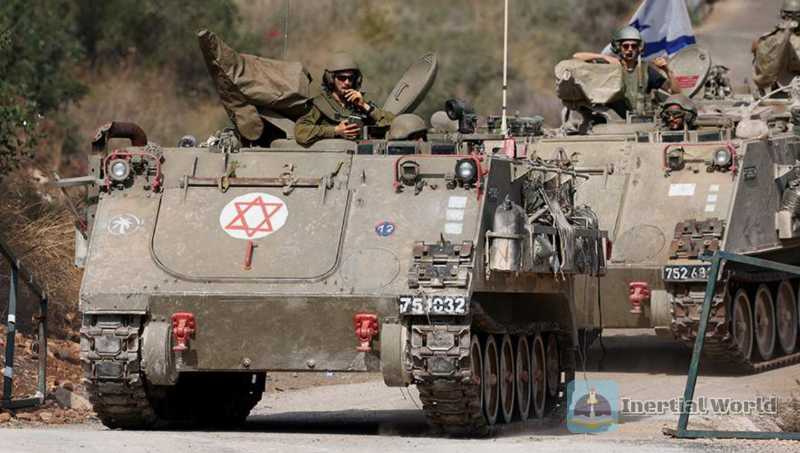

In 1970, Israel began to purchase more M113 armored personnel carriers to replace the aging M3 half-track armored vehicles, which dated back to World War II. Soon, Israel became the second largest user of the M113 series armored vehicles, with more than 6,000 M113s at its peak in the 1990s. And according to different versions of the M113, different nicknames were given. The basic model was called "Cheetah", and the urban warfare model equipped with explosive reactive armor was called "Zelda". By the end of the 1990s, with the large-scale retirement of the M113 equipped by the US Army, Israel became the number one user of the M113. However, although the Israel Defense Forces have always been highly dependent on the M113, and the M113 itself can still demonstrate its value in various local conflicts in the 21st century - for example, in the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, the protection level of the M113 aluminum armor provided to Ukraine by the West is considered to be comparable to the steel armor of the Soviet BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle, but slightly worse than the BMP-2. However, the Ukrainian army believes that the M113 is easier to maintain and travels much faster than Soviet infantry fighting vehicles. If necessary, the M113 can evacuate the battlefield faster than Soviet armored vehicles. But this still cannot cover up the reality that the M113 is too old. So in order to meet the needs of Israel’s future defense strategy transformation, the Israel Defense Forces launched the M113 replacement plan a few years ago. The result is the "Eitan" that will be officially put into service in 2023. However, the "Eitan" is not just a replacement vehicle for the M113. As the first wheeled armored vehicle owned by the Israel Defense Forces, it shows some meaningful changes
Main information of the "Eitan" wheeled armored personnel carrier
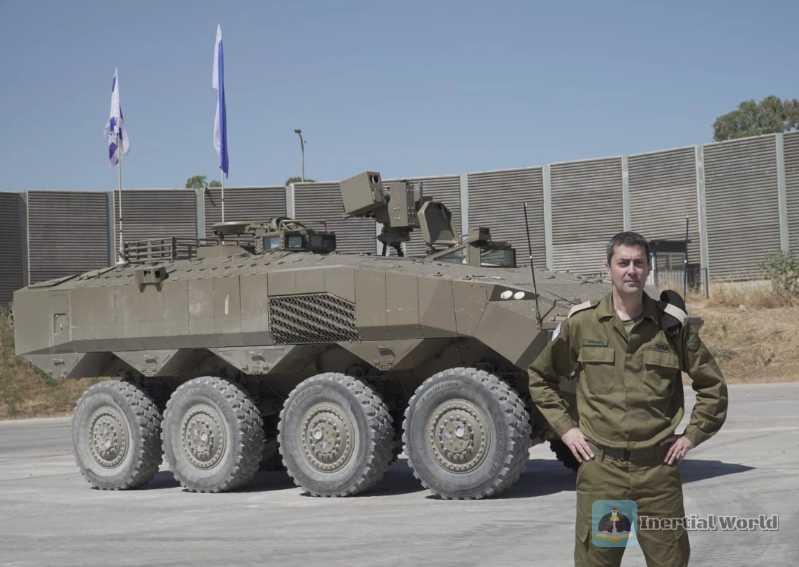
The "Eitan" 8x8 wheeled armored personnel carrier was developed by the Israel Tank Production Authority in 2015. The main contractor is the US Oshkosh Defense Company, and the subcontractors are Israel Aerospace Industries, Israel Military Industries and Rafar. The prototype of the "Eitan" was extensively tested from 2018 to 2022. The vehicle is 8 meters long, 3 meters wide, 3 meters high, and has a combat weight of 35 tons. During the development, Oshkosh Defense provided a mature design solution and borrowed many technologies from Israel’s "Merkava" main battle tank and "Tigress" infantry fighting vehicle, making its development work relatively smooth
The "Eitan" adopts the classic layout often used by modern wheeled armored vehicles, that is, the power compartment is in the front, the fighting compartment is in the middle, and the passenger compartment is in the rear. The body is welded with high-hardness armor. The driver is located on the left side of the front of the vehicle, and the power compartment is located on the right side of the driver. The interior of the vehicle adopts a compartmentalized design, and the entire power unit including the engine, transmission, cooling and ventilation system can be disassembled and replaced in a short time. The vehicle has sufficient armor protection, adopts an all-steel welded structure, and is equipped with armor plates composed of steel and ceramics, which are fixed by bolts. The "Eitan" has a smooth appearance and a flat structure, which helps to reduce the strength of radar signals. There are also measures to reduce infrared characteristics on the vehicle. In order to improve the protection, the front part of the "Eitan" adopts a large-angle bulletproof design, and the upper part of the body is made of frosted material to prevent the occupants from slipping when getting on and off the vehicle. The front headlight adopts an embedded design, deeply recessed in the upper front armor. This design can reduce the bullet-proof surface and reduce the chance of the headlight being hit by stray bullets. A V-shaped mine protection component is installed on the bottom of the vehicle to improve the mine protection capability. The bulletproof wheels enable the vehicle to travel a safe distance (more than 16 kilometers) at a speed of less than 50 kilometers per hour after being shot and exploded. The rear hatch of the vehicle is hidden in the guardrails on both sides, so that people can hide when getting off the vehicle. In addition, the flat body structure helps to reduce the strength of radar signals. The vehicle has excellent maneuverability, is equipped with a 750-horsepower turbocharged diesel engine, and is equipped with an 8-speed automatic transmission. The maximum road speed can reach 90 kilometers per hour, and the maximum driving distance can reach 900 kilometers. This gives it excellent maneuverability and off-road performance on the battlefield. Ride comfort is another highlight of "Eitan". The interior can accommodate 12 passengers, including the driver, the commander, the gunner and 9 infantrymen. In fact, "Eitan" emphasizes ride comfort in its design, and the cabin is designed according to ergonomic principles, so that the crew can persist in combat for a long time in a harsh combat environment. The fully sealed armored structure not only provides comprehensive protection for the carriers, including "nuclear, biological and chemical" defense, but also facilitates the installation of a high-power air-conditioning system, which is suitable for long-term combat in hot areas. Each passenger seat is equipped with a seat belt. The optimized suspension and shock absorption system greatly reduce the noise in the car. Achieve "silent" driving. The hydraulically controlled springboard-type rear door allows passengers to get on and off the vehicle quickly. The wide body provides passengers with a spacious and comfortable living and combat environment. The leather seat cushions and backrests are soft and comfortable, and the seat cushions can be folded up, further increasing the space of the passenger compartment passage. In addition, the vehicle is also equipped with a water tank to meet the soldiers’ drinking water needs during patrols and combat.

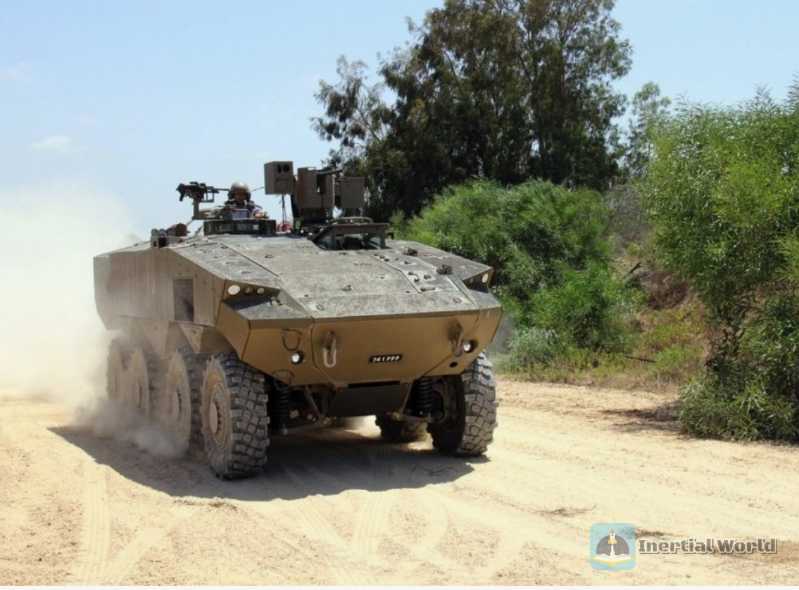
The weapons of "Eitan" are divided into light and heavy configurations. The roof of the former is equipped with a "Samson" small remote-controlled weapon station, and the main weapons include a 12 .7mm heavy machine gun and a 40mm automatic grenade launcher. Its optoelectronic devices include a daytime camera with magnification, a thermal imager and a laser rangefinder on the right side of the weapon station. It has stabilization and image enhancement functions, as well as moving target detection and tracking functions. The latter configuration has a "Samson" Mk2 remote weapon station installed on the roof, as well as a more complete sensor system. It can be equipped with a "Spike" series anti-tank missile launcher and a 60mm ultra-light mortar that can fire high-explosive fragmentation grenades and smoke bombs. The "Samson" Mk2 remote weapon station has day/night observation capabilities and high accuracy. It is equipped with a dual-degree-of-freedom sighting line stabilization system and a third-generation fire control system, which can effectively attack moving targets. In addition, "Eitan" is also equipped with an active protection system. Initially, it was planned to install the "Trophy" system developed by Rafael, which is a mature equipment installed on the "Merkava" MK4 and "Tigress" heavy armored transport vehicles. The US Marine Corps also purchased this system and installed it on the M1 main battle tank. However, "Eitan" finally chose the "Iron Fist" active protection system developed by Rafael. It uses active radar to search for incoming missiles, rockets and other threats. It can also install passive infrared detectors. After discovering the target, it launches fragmentation bombs through a small rotating launcher to intercept. Similar to the US military’s "Stryker" vehicle family, the "Eitan" tank will develop a series of models, such as self-propelled mortars, wheeled assault guns similar to the Italian "Centaur", missile launchers, battlefield command posts, rescue vehicles and other models.
Reasons for giving up tracks
"Eitan" means "firmness and longevity" in Hebrew. It is not difficult to imagine what kind of expectations are given to the new generation of "Eitan" armored personnel carrier named after it. It is particularly noteworthy that for the Israel Defense Forces, the acceptance of the "Eitan" not only means the replacement of the M113, but also means that the Israel Defense Force has taken a big step into the wheeled era. Generally speaking, compared with tracked armored vehicles, wheeled armored vehicles have the advantages of simple structure, low cost, low failure rate, low fuel consumption, long range, and can be quickly deployed using existing road conditions. But at the same time, the shortcomings of wheeled armored vehicles cannot be ignored. For example, the off-road capability of wheeled armored vehicles is not as good as that of tracked armored vehicles. In terms of crossing ditches, climbing vertical walls, and climbing steep slopes, wheeled vehicles are still far behind tracked vehicles. In addition, the platform stability of wheeled vehicles is not high. Even for wheeled vehicles with 8 sets of suspension wheels, the stability when off-road is worse than that of tracked vehicles with usually double-digit suspensions.
In fact, as early as the 1920s and 1930s, the Soviet Red Army Armored Forces Inspector, Tukhachevsky’s close comrade-in-arms, Konstantin Bronislavovich Kalinovsky, had a brilliant discussion in the article "Problems of Motorization and Mechanization of Modern Armies" (the article was originally published in the collection of works published by the Soviet Communist Academy (War Problems Research Class) in 1931): "No matter how strange it is, in general, motorized corps of the ordinary corps type equipped with corresponding reconnaissance equipment have greater Independence. If we make a comparison between motorized and mechanized corps in this regard, we will see the situation. Now, when the motorized corps implements campaign maneuvers along roads, it will have an advantage over the mechanized corps, because wheeled propulsion devices have greater reliability when driving than tracked propulsion devices. However, when implementing campaign maneuvers without roads, the advantage will shift to the mechanized corps, because tracked vehicles can maintain average speed on bad roads more reliably than wheeled vehicles. If it is about the maneuver itself, then the situation will be the same: if this maneuver is carried out on the corresponding road network, the advantage will still be on the side of the motorized corps rather than the mechanized corps.

From the perspective of offensive conditions, the mechanized corps has higher capabilities than the motorized corps, because the motorized corps becomes an ordinary corps from the moment its troops get off the vehicle (if it is reinforced by armored tank units, its assault power will be increased accordingly). In this way, for the motorized corps, there will be a break between campaign maneuvers and tactical maneuvers, because it is necessary to get the soldiers off the vehicle and then deploy them into combat formations in the manner of infantry. The motorized corps has a strong ability to hold areas. The power of the mechanized corps lies in movement and firepower. If we talk about the degree of being restricted by conditions, then the advantage will certainly be on the side of the mechanized corps. Mechanized Corps, equipped with tracked vehicles, undoubtedly has a greater ability to pass... In terms of operational persistence, the advantage is in the motorized corps, because it actually has the same combat capabilities as any ordinary corps, while the mechanized corps is more limited in this regard due to its operational characteristics and vehicle maintenance characteristics (such maintenance will quickly make personnel exhausted). Although this assertion is made 90 years ago, with the passage of time, the technical performance of today’s combat vehicles has also undergone tremendous changes. As combat platforms, the technical and tactical performance characteristics of wheeled vehicles and tracked vehicles have tended to merge, but the fundamental difference between wheeled vehicles and tracked vehicles remains. Simply put, the stronger the protection, the more complex the terrain, and the more powerful the firepower, the more suitable it is for tracked vehicles to appear, and vice versa. So, with the introduction of the new generation of "Eitan" armored personnel carriers as a symbol, the armored mechanized forces of the Israel Defense Forces began to transform from a full tracked force to a wheel-track mixed force. What is the reason behind this? This is actually not difficult to understand. To put it bluntly, this means that within the foreseeable time, Israel believes that the possibility of facing a high-intensity ground war will be greatly reduced.
For example, among the traditional adversaries that border Israel directly, Egypt normalized its relations with Israel as early as 1979. After the "July 3" incident in 2013, former Egyptian Defense Minister Sisi began to take charge of Egypt’s highest power and was elected as the country’s president. Since then, Egypt-Israel relations have begun to heat up sharply. At present, the two countries have established a new bilateral relationship with the basic characteristics of a quasi-alliance based on security cooperation and close strategic cooperation. Egypt and Israel have launched a series of close strategic cooperation and even ceded part of their sovereignty to each other. For example, Egypt allowed Israel to carry out cross-border strikes many times. The level of cooperation between the two countries has surpassed the level of ordinary state-to-state relations. Israel also gave Egypt various rewards, so much so that Israel actively lobbied the US Congress for Egypt to purchase US "Apache" armed helicopters. This was a rare case of "the first time in history that Israel lobbied to ensure the supply of weapons to Arab countries." This is enough to show that Egypt-Israel security mutual trust has been greatly improved since Sisi came to power. Israeli Energy Minister Yuval Steinitz once said that Egypt-Israel security cooperation is better than any period in history. "Coordination and information exchange are at the highest level, and senior military commanders of the two countries communicate almost every day."
In addition to Egypt, Jordan has also long achieved reconciliation with Tel Aviv. Jordan is the second Arab country to sign a peace agreement with Israel after Egypt. Jordan has always been more "rational" in its relationship with Israel due to security and other factors, and the two sides have always maintained relatively close contact. There is a lot of cooperation between the two countries. According to the peace agreement signed between them, Israel provides Jordan with a large amount of fresh water, which is a resource that Jordan is extremely short of. A railway connecting the Jordanian capital Amman and the Israeli Mediterranean city of Haifa has also been built. Israel has also helped Jordan to a large extent solve the problem of a large number of refugees and terrorist attacks from Syria. For Israel, Jordan is located to the east of Israel. Jordan, a monarchy, is an important buffer against terrorist attacks from the east. Jordan has done a good job in curbing terrorism and has effectively prevented Israel’s hostile forces from approaching Israel from the east. Jordan and Israel even have some military cooperation. Some of the AH-1 attack helicopters equipped in the Jordanian Air Force were transferred from the Israel Defense Forces to the Jordanian army for use. To some extent, Jordan and Israel are strategic partners, secretly taking care of each other’s important interests.
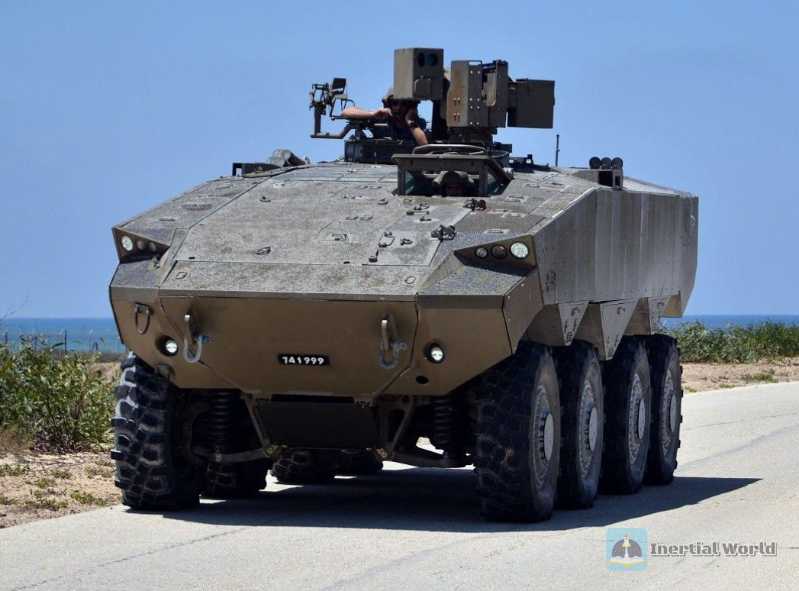

As for Syria, another traditional opponent that directly borders Israel, it has been hit hard in years of civil war. Although the current Syrian war, which has lasted for more than a decade, has entered an era of reconstruction: the extremist organization "Islamic State" that once ravaged Syria has gradually disappeared under the attack of the international community; the Syrian government forces launched a nationwide counterattack, gradually compressing the Syrian anti-government forces in the northwestern Idlib Province and the northern part of Aleppo Province; with the help of the international community, the selection of members of the Syrian New Constitution Committee is also gradually underway, and the Syrian government and opposition political groups are also in dialogue under multiple international peace mechanisms such as Geneva, Astana and Sochi. But even so, the current Syria is still a chessboard reflecting the continued tension in the Middle East. In fact, Syria, once a regional power, is still divided into regions controlled by different forces, each of which responds to the interests and ideology of its international sponsors. With the support of Russia and Iran, Bashar al-Assad’s government was able to reconquer two-thirds of the country’s territory. Armed opposition militias, including several organizations listed as terrorists by the United Nations, are trapped in the northwestern Idlib Province, where they receive military, logistical and economic support from neighboring Turkey. The northeast is controlled by Kurdish militias supported by the United States. That is to say, after ten years of turmoil, Syria not only has domestic factions at odds with each other, but has also evolved into a "wrestling field" for great power games. World powers led by the United States and Russia, as well as regional powers such as Iran, Israel, and Turkey, all have spheres of influence and interests in Syria. Therefore, since 2019, although the Syrian government has successively announced dozens of reconstruction plans, the huge amount of funds required is difficult to raise, and the bidding for large-scale infrastructure projects and international investment promotion are progressing slowly. Such a Syria will obviously be difficult to restore to the tough opponent that has repeatedly fought with Israel on the battlefield in history in the foreseeable future... From Egypt, Jordan to Syria, opponents directly bordering Israel have either turned enemies into friends or have been deprived of their offensive capabilities. This naturally means that Israel’s geopolitical environment is favorable and the national security situation has been greatly improved. As for Iraq, the situation is similar to that of Syria. The entire country has been severely damaged in years of war, and it does not directly border Israel.
Of course, Iran’s security threat to Israel still exists. But this issue needs to be viewed from a deconstructionist perspective. Iran and Israel are also not bordering each other. Its security influence on Israel is achieved through long-range missiles or proxy wars. However, considering that Iran has not yet crossed the nuclear threshold, its long-range missiles are actually extremely limited in front of Israel’s anti-missile defense system built with the whole country’s strength. Israel’s counterattack on Iran’s homeland is mainly completed by the Air Force, and the Army is useless. As for Iran’s harassment of Israel by proxy, to be precise, it is a guerrilla war against Israel by funding organizations such as Hezbollah and Hamas, which actually belongs to the category of low-intensity irregular warfare. Moreover, with the normalization of relations between Israel and Arab countries such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, an "Israel-Arab" anti-Iran alliance is taking shape. For example, the normalization of relations between Israel and Saudi Arabia is of great significance.

In his book "The Origin of Alliances", American scholar Stephen Walt put forward different views on how countries choose allies. He believes that countries choose to form alliances in order to balance threats, which mainly come from four aspects: comprehensive strength, geographical proximity, offensive capabilities, and aggressive intentions. In reality, Saudi Arabia and Israel have come close and formed a paramilitary alliance out of consideration for Iran, a common regional threat. Based on its comprehensive strength and religious status, Saudi Arabia is generally regarded as the leading country in the Arab world and has a special status in the entire Islamic world. However, there are serious sectarian conflicts between Saudi Arabia and Iran. Saudi Arabia has always been ensuring its absolute leadership in the Arab world, but Iran has taken every opportunity to continuously infiltrate the Arab world, including providing military and financial support to Shiite forces and some Sunni forces in the Middle East. In Saudi Arabia’s view, this has seriously challenged Saudi Arabia’s leadership in the Arab world. Some people believe that the degree of hostility between Iran and Saudi Arabia is higher than that between Iran and Israel. Iran’s strong rise has been jointly identified by Israel and Saudi Arabia as the biggest threat to national security. The two countries have reached a strategic consensus and formed a "security strategic alliance" to jointly contain Iran. Similarly, in the normalization of relations between Israel and the UAE, containing Iran is also an important part. The geopolitical landscape of the Middle East changed dramatically in 2011. Iran’s growing influence in Iraq, Syria, Lebanon and Yemen has put Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Kuwait on pins and needles. Iran, which adheres to the Shia principle of "rule by the clergy", is not only in opposition to the Gulf Arab countries that respect Sunni Islam and are mainly Arab, but the two sides also have differences on practical issues such as Syria and Yemen. It is precisely because of Iran, a common enemy, that Israel and the UAE, two former enemies, have come together. Under the matchmaking of the United States, the two sides had already launched substantial military cooperation long before Israel and the UAE established diplomatic relations. For example, in June 2017, leaked emails showed that the UAE and Saudi Arabia cooperated with Israel to fight Iran. The UAE has established a close relationship with the pro-Israel neoconservative think tank Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD) with the aim of "finding ways to hinder Iran’s capabilities." In July 2017, the UAE hosted and mediated a meeting between Israeli intelligence and the Libyan National Army to negotiate Israel’s military assistance to the regime. The meeting was supported by the UAE in the second Libyan civil war. In March 2018, Netanyahu met with UAE Ambassador Otaiba at a restaurant in Washington to discuss Iran. In September 2018, the UAE held secret talks between Israeli and Turkish officials in Abu Dhabi to discuss restoring relations between the two countries. In 2019, the United States remained silent on Iran’s attack on Saudi Aramco facilities, which further deepened the alliance between Israel and the UAE to suppress Iran. It is generally believed that the "Israel-Arab" anti-Iran alliance formed by Israel, Saudi Arabia, the UAE and even Egypt will largely contain and consume Iran’s national strength, which will naturally lead to a reduction in its ability to intervene. Then in a greatly improved geopolitical security environment, since the possibility of a high-intensity ground war has been greatly reduced, it is an inevitable choice to cut defense costs as much as possible. As one of the measures, there is a logical explanation for the unprecedented replacement of the M113 by a wheeled armored vehicle such as the "Eitan" instead of a tracked vehicle.
Impact on Israel
Israel is small in area and has no strategic depth. After its founding in 1948, Israel was like an "isolated island" surrounded by hostile Arab countries and the Islamic world. The living environment was extremely harsh. Until the Middle East changes in 2011, the only Arab countries that formally established diplomatic relations with Israel were Egypt and Jordan. The establishment of diplomatic relations with Egypt, the "leader" of the Arab world, in 1980 was a major diplomatic victory for Israel, but Israel did not produce a positive domino effect in Arab countries. Egypt-Israel relations also stopped at cold peace due to the setbacks in the Israeli-Palestinian peace process, and Jordan, a small country, failed to help Israel achieve a new diplomatic breakthrough. But the so-called one time is another time. As one of the biggest beneficiaries of the Middle East changes since 2011, there is no doubt that Israel is currently in the most relaxed national security environment since its founding. The greatly improved national defense situation will naturally lead to corresponding adjustments in the national defense force construction policy. For example, with the threat of high-intensity ground warfare greatly reduced, Israel’s defense construction resources have further tilted towards the Air Force and Navy, while the Army has begun to reshape its capabilities to cope with the needs of gray zones and hybrid warfare. The prominent features of hybrid warfare are "hybridity" and "asymmetry". In terms of subject, the protagonists of the war are a mixture of state actors and non-state actors, and the two sides of the war do not need to be equal; in terms of fields, politics, economy, military, culture, information, etc. are all-encompassing. War can occur in one of these fields or in multiple fields at the same time. The choice of combat fields by the two combatants does not have to follow the principle of equality; in terms of means, there are both the use of military force and diplomatic mediation, as well as the manipulation of information and public opinion...-a series of mixtures blur the boundaries between war and peace, constantly challenge people’s cognition of modern warfare, and make the struggle between actors unprecedentedly complex. In terms of concept, hybrid warfare is a product of the new century, but the ideas of "mixture" and "ambiguity" it contains are not new. Its essence is to use the gray area between war and peace as an entry point to achieve strategic goals through the comprehensive use of different means. Of course, different countries and different viewpoints have different understandings of hybrid warfare. Israeli political and military elites generally believe that hybrid warfare is a highly mixed combination of traditional and unconventional warfare, posed by the enemy’s flexible and comprehensive use of conventional weapons, unconventional tactics, terrorist attacks and criminal activities in the combat space. The prominent features of hybrid warfare are "hybridity" and "asymmetry". In terms of subject, the protagonists of the war are a mixture of state actors and non-state actors, and the two sides of the war do not need to be equal; in terms of fields, politics, economy, military, culture, information, etc. are all-encompassing. War can occur in one of these fields or in multiple fields at the same time. The choice of combat fields by the two combatants does not have to follow the principle of equality; in terms of means, there are both the use of military force and diplomatic mediation, as well as the manipulation of information and public opinion... A series of mixtures blur the boundaries between war and peace, making the struggle between actors unprecedentedly complex. The essence of hybrid warfare is to achieve political goals by carrying out minimal armed strikes against the enemy. There are many ways to achieve this goal, such as destroying military and economic potential, creating information and psychological pressure, and even domestic opposition, guerrillas and sabotage activities. It is precisely driven by this cognition that the Israeli Army began a corresponding strategic transformation. As the first wheeled armored personnel carrier equipped on a large scale by the Israel Defense Forces, the "Eitan" also has a strong iconic flavor. The era of "Eitan" is about to begin.
Conclusion
Israel is such a nation. It has a long history and is tenacious. It has endured many hardships in the long river of history. After overcoming various difficulties, it was founded around 1948. After the founding of the country, it proved itself with several tragic but beautiful turnarounds, allowing itself to gain a firm foothold in an environment surrounded by powerful enemies.
But at the same time, Israel slowly developed towards the Spartan extreme martialism. Israel is the most powerful country in the Middle East, but the fundamental reason why Israel can persist in the Middle East is the support of the United States. Without the support of the United States, Israel will be swallowed up by the surrounding Arab nations even if it is more capable. With the decline of the United States’ national strength, if Israel continues to be militaristic, its future will be worrying.
When the Israelis first founded the country, they were known for their ability to judge the situation. Their national defense construction has always been adjusted according to the assessment of the national security environment. It is precisely because of this that the Israel Defense Forces have their own unique understanding of weapons. This is reflected in the new generation of Eitan armored personnel carriers, which have a different flavor. Although the Eitan may not be outstanding compared with mainstream wheeled armored vehicles in terms of technology, as a regional equipment with a very clear targeting, the Eitan is just right for the Israel Defense Forces.