On March 4, 2024, the French Armed Forces published a list of military equipment inventories supplied to Ukraine from February 24, 2022 to December 31, 2023. According to statistics, the French government has provided Ukraine with a total of 2.615 billion euros worth of military equipment, in addition to an additional 1.2 billion euros to the European Peace Fund (EPF), with a total support of more than 3.8 billion euros as of December 31, 2023. Although most of these weapons and equipment have been reported and known before, their quantity has not necessarily been disclosed, and their complete list has not been disclosed. There are even some equipment that the outside world does not know for sure whether they are fighting in Ukraine. The authoritative list of weapons and equipment released by France this time is comprehensive. Let’s take a look at what "family assets" France has taken out to support Ukraine. It is worth emphasizing that in addition to direct military and financial assistance to Ukraine, France has also participated in the training of the Ukrainian army. Nearly 10,000 Ukrainian soldiers have been trained by French and Polish military personnel, reflecting France’s determination to enhance Ukraine’s defense capabilities through training and skills development programs. While supporting Ukraine, France is also actively involved in strengthening security in Eastern Europe. The country has ground deployments in Romania and Estonia and temporary air deployments in Lithuania and France. In addition, France maintains a maritime presence in the Baltic Sea and the Mediterranean.
Overview of military aid
In total, France provided the Ukrainian army with approximately 50 different weapons and military equipment between February 24, 2022 and December 31, 2023. The equipment provided by France includes advanced systems such as air defense combat platforms, armored vehicles and advanced artillery vehicles, highlighting Ukraine’s significant efforts to enhance its military response capabilities.
In addition to these necessities, France also provided a variety of personal equipment including optical and communication systems, which improved the tactical effectiveness of Ukrainian forces. This support also extends to maritime and medical equipment, demonstrating a comprehensive approach aimed at addressing the various needs of the Ukrainian armed forces in the conflict.
Subsequently, we will use a list to select the more typical and advanced models from the various weapons and equipment on the list of French aid to Ukraine.
AT4 anti-tank rocket launcher (a total of 1,002 units were provided to Ukraine)
AT4 is used to engage armored vehicles with reactive armor, lightly armored wheeled vehicles and light bunkers. It can fire in a confined space as long as certain size and volume conditions are met. The weapon is designed for close-range combat, and the ammunition is designed for one-shot shooting.
AT4 uses the principle of recoilless gun firing. The rocket launcher includes a rocket launcher, aluminum alloy, shoulder straps, and front and rear protective sealing covers. The simple mechanical sight consists of a mountain-shaped front sight and adjustable concentric inner and outer ring rear sights. A low-light sight and an optoelectronic fire control system can also be used.

AT4 fires hollow charge armor-piercing shells, using aluminum or copper-aluminum composite charge caps. The armor-piercing process is divided into several stages, including contact, burning, armor-piercing, and armor-piercing effects. The armor-piercing effect can produce peak high pressure, high heat and a wide range of killing fragments in the vehicle body, accompanied by blinding strong light and burning effects.
In response to the request of the Swedish Army, the Swedish FFV Arms Company began to develop the AT4 84mm rocket launcher in 1976 to replace the old 74mm rocket launcher. In the light anti-tank weapon selection test conducted in the summer of 1983, the rocket launcher was selected for its excellent performance, and 270,000 were ordered from Sweden in September 1985. Later, the American Ariante Technology Equipment Company obtained the franchise production rights, and after redesign, the AT4 was adopted by the US military and called the M136 anti-tank grenade launcher.
Milan anti-tank missile (currently 3 units have been delivered)
Milan is a portable anti-tank missile system with a maximum effective range of 2,000 meters. It can penetrate more than 500 mm of rolled homogeneous armor. Its wired guidance system enables the operator to engage stationary or moving targets and adjust the missile’s trajectory, making it a key asset in defending against enemy armored threats.
Milan is a second-generation light anti-tank missile developed by France and Germany. It was developed in 1963 and equipped to the troops in 1974. It adopts visual aiming, infrared semi-automatic tracking, and wire transmission command guidance. The projectile diameter is 116 mm, the projectile weight is 6.7 kg, the range is 2,000 meters, and the vertical penetration of steel armor is 690 mm. In 1983, the basic "Milan" was improved, and the warhead diameter increased from 103 mm to 115 mm. The improved "Milan"-2 will be further improved to use a tandem warhead to deal with composite armor and reactive armor. The improved Milan-2 is called Milan-2T.
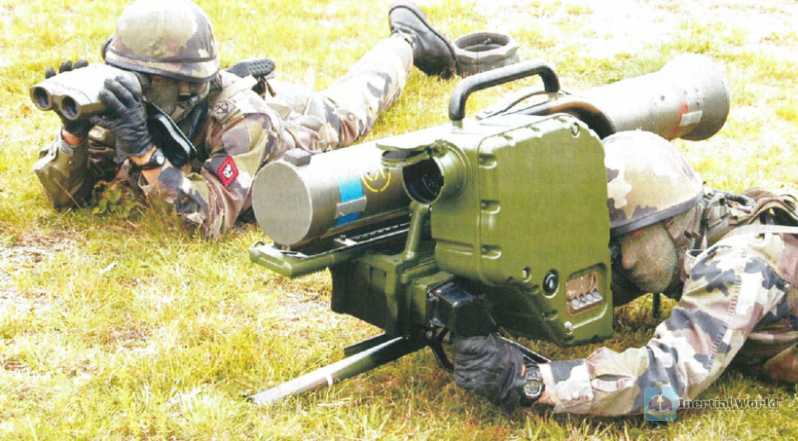

Milan is used for ground launch; the heavier HOT is used for vehicle or helicopter launch. The earliest Milan (Milan-1) entered service in 1972, with a bullet diameter of 103 mm and an armor penetration depth of 650 mm. It was put into use in the Lebanese War in 1976 to deal with T-55 and T-72 tanks. At that time, no one realized the advanced nature and flexibility of the Milan missile program, and its advantages have only been revealed today. Because many military operations today are carried out in the streets and alleys, the Milan missile has a minimum range of 25 meters, which is just the ideal weapon for street fighting. The repeated use of the Milan missile in the African battlefield, the Falklands War and the Gulf War has proved its operational flexibility. It is reported that the Milan missile can not only deal with tanks, but also shoot down helicopters and patrol boats. In the Gulf War, the Milan missile achieved a good record against Scud missile launchers.
In 1984, the Milan-2 was successfully developed. The Milan-2 uses an improved 115mm armor-piercing projectile with an armor penetration depth of 1000 mm. In 1991, the Milan-2T model was launched. Milan-2T, with a 30mm advance warhead charge added to deal with targets with anti-explosion armor. In 1995, Milan-3 was introduced. Milan-3 has a pulsed xenon infrared beacon operating at about 0.9 microns and a thermal imaging night vision device to improve its anti-interference ability and enable night operations. The range of each type of Milan missile is 2,000 meters.
In addition to being produced in France and Germany, Milan missiles are also produced in the UK, India and Italy. More than 330,000 Milan missiles and more than 10,000 launchers have been produced for 43 countries. The model being produced is Milan-3, which was ordered by France, Germany and two other countries.
From the current point of view, the number of Milan anti-tank missiles supplied to Ukraine is only 3 sets, which can be said to be a drop in the bucket. In the battlefield of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, to attack enemy tanks and armored vehicles, the main method is to use the more "bulky" "Javelin" anti-tank missile.
TRF1 (6 guns supported)
TRF1 is a towed 155mm gun with a maximum range of about 30 kilometers when using extended-range ammunition. Its accuracy and powerful ballistic capability enable it to effectively provide fire support and interception at a considerable distance, thereby helping ground forces in offensive and defensive operations. The gun was developed by the French Ground Weapons Industry Group in 1976, and the French Army plans to order 180 guns. It was officially equipped with the artillery regiment of the French infantry division at the end of 1984.
TRF1 howitzer, equipped with a 155mm caliber and 6.2-meter-long barrel, can fire 155mm caliber high-explosive shells with a range of 24 kilometers, and the range can be up to 29 kilometers using extended-range ammunition. The TRF1 howitzer weighs 10 tons and has a two-wheeled frame that can be towed by a motor vehicle. The TRF1 howitzer has a rate of fire of 6 rounds per minute. The gun can be driven on a 60% slope when towed. The TRF1 howitzer uses a hydraulic sight, and the horizontal shooting range is 445 mils to the left and 675 mils to the right.
Caesar vehicle-mounted howitzer (30 units supported)
Caesar self-propelled howitzer is a truck-mounted self-propelled howitzer developed by the French Ground Arms Industry Group (GIAT) and the Anjan Biedan-Laur Group with a wheeled truck equipped with a 155mm 52-caliber gun and an automated fire control system. Caesar uses the U-2450L (Unimog) six-wheel light truck chassis of Daimler Benz or the Renault Sherpa 10 six-wheel light truck chassis. The GIAT 155mm 52-caliber gun is mounted at the rear of the vehicle body, with an open design and no turret protection. The combat weight of the Caesar is only 17.65 tons. When fully loaded with ammunition and ready for combat, it can still be tactically deployed by a C-130 transport aircraft together with all operators, so it is very suitable for rapid reaction forces.
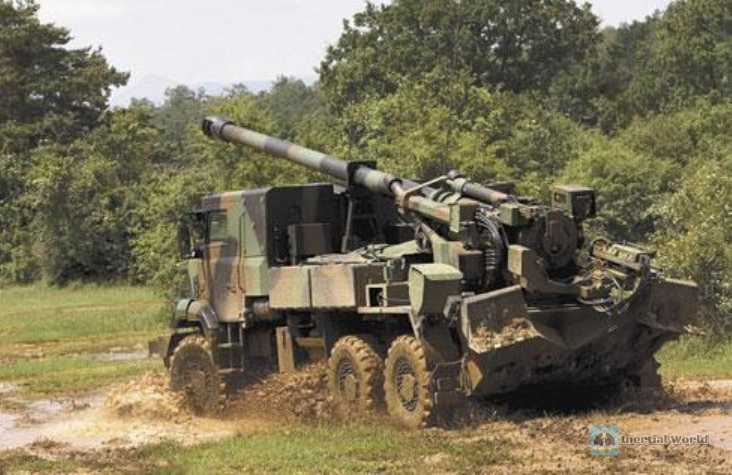

CAESAR 155mm self-propelled howitzer combines mobility, range and firepower. When using extended-range ammunition, the combat range can reach 40 kilometers. It is installed on a 6x6 truck chassis and can provide excellent mobility, rapid deployment, and the ability to perform shooting and sliding maneuvers on different terrains, reducing the sensitivity to counter battery fire. The French army equipped this batch of Caesar howitzers supporting the Ukrainian army with 300,000 rounds of 155mm ammunition, which can be said to be relatively sufficient ammunition.
The Caesar completed its pre-production preparations in 1998 and was shipped to Malaysia for testing in 1999. However, it was not until the beginning of this century that it received an order from the French Army. From 2002 to June 2003, five pre-production models were built for testing by the French Army. In the second half of 2003, the French Army decided to divert more funds originally intended for upgrading the AUF-1 155mm tracked self-propelled howitzers in service to purchase Caesar self-propelled howitzers, and ordered a total of 72 Caesars (the French Army has a total demand for 120 Caesars, so additional purchases may be made) to replace the current TRF-1 155mm 39-caliber towed howitzers.
The Caesar uses a 155mm 52-caliber gun body, which is basically an improvement on the French Army’s original TRF-1 155mm 39-caliber howitzer. The design of the Caesar self-propelled howitzer is to cooperate with rapid reaction forces, such as focusing on independent operation capabilities. The truck chassis is powered by an OM-366 upright six-cylinder diesel engine with a maximum horsepower of 260, which enables it to have a maximum road speed of more than 100 kilometers per hour, a maximum off-road speed of 50 kilometers per hour, and a cruising range of 600 kilometers. The Caesar’s cockpit is armored and can withstand the attack of shell fragments. The Caesar has a crew of six people, including a driver and five gun crew members, which is much less than the towed artillery crew of more than 10 people; the crew sits in the cockpit when driving, and needs to get off the vehicle to operate the gun in an open environment when shooting.
Caesar has a wide range of ammunition options, including NATO standard high explosive (HE), anti-personnel/materials bombs, Ogreshe1l series submunitions, low-resistance long-range full-bore bottom-row grenades (ERFB-BB/HE) and guided anti-armor ammunition. The standard Ogre shell has a range of 35 kilometers. It is a scattering ammunition that can scatter 378 submunitions over an area of 3 hectares. In addition, Ogre shell can also use high-explosive bombs, anti-personnel bombs, arson anti-oil depot bombs and other warheads; low-resistance long-range full-bore bottom-row grenades have a range of 42~50 kilometers.
LRU (M270) rocket launcher system (4 sets have been delivered)
M270 self-propelled rocket launcher is a multiple rocket launcher developed by the United States. This type of rocket launcher consists of three major parts: tracked launcher, launch box and fire control system. The M270 self-propelled rocket launcher was put into production in 1983 and began to be equipped with the US Army. The US Army has an M270 rocket launcher battalion equipped with 27 guns; the armored division and mechanized division have 1~2 companies equipped with 9 guns. It is mainly used to kill enemy manpower, anti-artillery operations, anti-armor operations, etc. The Taiwan Army borrowed its design ideas and developed the "Thunder" 2000 multiple rocket launcher, which also uses the "loading and launching box" form to supply and shoot, equipped with three different calibers and ranges of rockets, as its backbone firepower for anti-landing operations. The M270 self-propelled rocket launcher is in service with the US Army and is equipped by many other countries. It is also a NATO standard multi-mission rocket launcher system. As a NATO country, the French Army is naturally equipped with the M270 system.
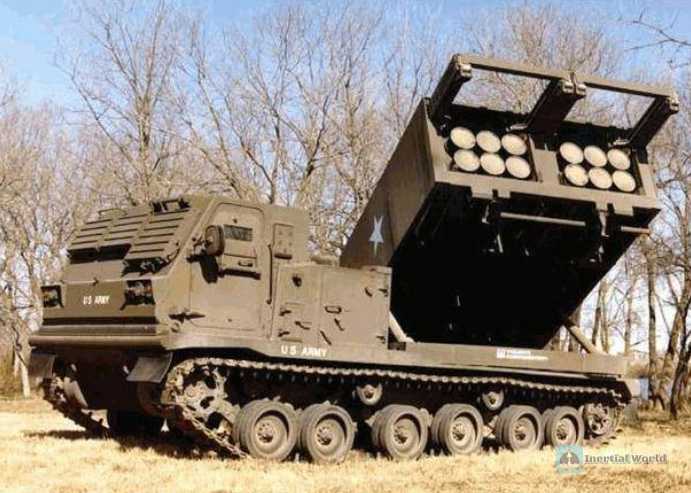

A feature of the M270 self-propelled rocket launcher is that there is no launch track. Rockets are fired directly from containers. Each disposable container holds 6 rockets. Rockets can be stored in containers without any maintenance for up to ten years. The vehicle carries 2 containers with a total of 12 rockets. The gun uses standard 227mm high-explosive fragmentation rockets, which are 3.96 meters long and weigh 307 kilograms. Both clusters of M270 launch rockets, equipped with anti-tank submunitions and AT2 anti-tank mines. The warheads are interchangeable. The new gun can fire newly developed guided ammunition with a range of 60 to 100 kilometers.
LRU (M270) MLRS is capable of firing devastating rockets at a distance of up to 70 kilometers, depending on the type of ammunition used. It can quickly cover a wide area with high-explosive warheads or submunition warheads, which makes it very effective against enemy concentrations, defensive positions and regional targets, providing a huge force multiplier for artillery units.
Crotale NG (2 sets delivered)
Crotale NG is also known as the "Sidewinder" system. The French "Sidewinder" NG air defense missile system uses Lockheed’s VT-1 missile. The French Air Force is currently equipped with the square-type "Sidewinder" NG type. Crotale NG is a mobile, all-weather, low-altitude short-range air defense missile developed by France. It is used to attack low-altitude and ultra-low-altitude fighters, armed helicopters, etc. It can also be used to defend airports, ports and deal with tactical missiles. Developed in 1964 and equipped to the troops in 1971. The full weapon system consists of a search command unit and a launch guidance unit. The projectile has a diameter of 150 mm and a weight of 85 kg. It uses radio command guidance and three-point guidance.
CrotaleNG is a highly mobile air defense system designed for short- and medium-range operations, capable of targeting threats at an altitude of 5,000 meters and 15 kilometers away. It is equipped with a radar system with rapid target acquisition and tracking capabilities, ensuring a rapid response to air threats. Its adaptability and seamless integration with existing defense networks make it ideal for protecting fixed facilities and mobile forces from air attacks.

Radar GM200 (1 unit delivered)
GM200 was developed by Thales of the Netherlands in 2011. It is called Ground Master 200, or GM200 for short. With its excellent performance, the radar quickly attracted the attention of the global military community. It can not only accurately detect various targets from birds to windmills, but also has intelligent differentiation capabilities, easily filtering out irrelevant targets according to the needs of the operator. The Royal Netherlands Army took the lead in purchasing nine GM200 radar systems, which are planned to be deployed in the Fire Support Command, six of which are used in field artillery units and three in air defense units. In the long run, it is also planned to purchase nine additional systems, doubling the number of radars in the two departments.
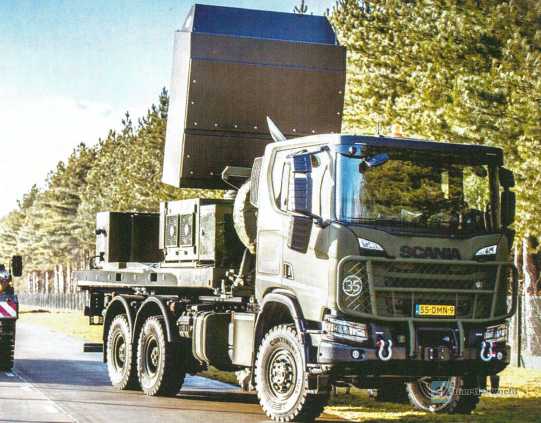

On the battlefield, the value of the GM200 radar system cannot be ignored. It can detect rockets and shells launched by the enemy in just a few seconds, quickly calculate the launch coordinates, and provide accurate information for anti-artillery fire. By cooperating with other radars deployed in different locations, it can effectively avoid enemy fire strikes. In addition, the GM200 radar system can quickly calculate the trajectory, impact point and launch point, and quickly transmit the information to other radars, artillery and other troops to achieve efficient coordinated operations.
In addition to the Netherlands, countries such as France, Norway, Denmark and Lithuania have also purchased this advanced radar system.
The radar is a versatile, multi-mission radar system known for its detection range of up to 250 km. It has the ability to track all types of aerial threats, from advanced fighters to small, low-flying targets. With its mobility, the radar system can be quickly deployed and repositioned, providing flexible support for air defense operations and improving situational awareness across the battlefield.
MISTRAL Mistral Air Defense Weapon System (6 units delivered)
MISTRAL Mistral Missile System is a portable air defense system (MANPADS) designed for short-range operations, capable of striking targets at an altitude of 3,000 meters at a distance of 6 kilometers. Its infrared guidance system enables enhanced fire-and-forget capabilities, increasing its effectiveness against low-flying aircraft and helicopters. Mistral’s portability and user-friendly operation make it ideal for rapid deployment in different combat environments.

Mistral missile is a multi-purpose air defense missile developed by France in 1980 according to the different requirements of the three French armed forces. It can be used in conjunction with anti-aircraft guns and other weapons, or it can perform air defense tasks alone. It is mainly used to deal with low-altitude and ultra-low-altitude targets, and was equipped to the troops in the late 1980s. At present, it is used in more than 20 countries and regions in the world.
The main technical features are: ① It adopts a multi-element infrared seeker with high sensitivity. For the first time, it uses indium antimonide quaternary sensitive devices and digital signal processing devices, which can intercept fighters at a distance of 6 kilometers and helicopters at a distance of 4 kilometers before launching, and has omnidirectional attack capabilities.
②The aerodynamic layout is reasonable, the speed is fast, and the maneuverability is strong. ③Laser proximity fuze and trigger fuze are used at the same time to ensure the accurate detonation of the warhead.
④The warhead is powerful. Compared with the general portable air defense missile, the 3 kg warhead has a significantly greater power and can penetrate a 6 mm thick steel plate at a distance of 50 cm. The warhead adopts prefabricated fragmentation technology and contains 185 tungsten alloy balls with a diameter of 2.5 mm. After detonation, it penetrates the target shell at a dispersion angle of 15 degrees and a speed of 1500 meters per second, with an effective killing radius of 3 meters.
⑤Easy to operate and short reaction time. The system is operated by two people and can be put into combat in 1 minute in an emergency.
Basic data are: length 1850 mm; bullet diameter 92.5 mm; wingspan 190 mm; bullet weight 18.4 kg; combat weight 21.4 kg; maximum speed 2.6 Mach; maneuvering overload 40g; maximum range 6 kilometers.
SAMP/T air defence system (1 unit delivered)
SAMP/T, the acronym for Sol-Air Moyenne Portée/Terrestre (Medium Range Surface-to-Air/Terrestrial), is an air defence missile system built by the Italian-French consortium Eurosam, which includes MBDA France, MBDA Italy and Thales.
It is a "theatre" system, i.e. short/medium range, capable of protecting sensitive locations (ports, airports, cities, troop concentrations, etc.) from attacks by cruise missiles, aircraft (manned and unmanned) and tactical ballistic missiles.
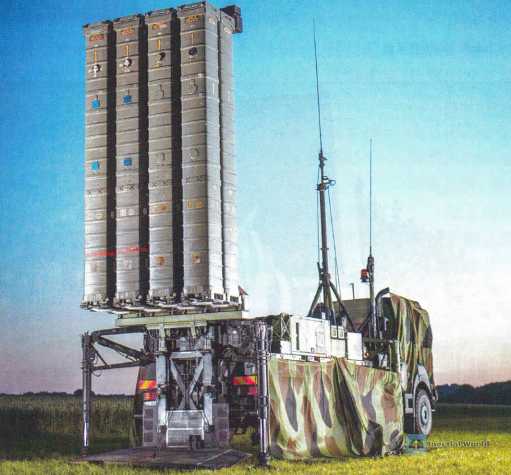

France and Italy jointly launched the development of the SAMP/T and Aster family of missiles in 1988 under the FSAF (Family of Surface-to-Air Systems) program. SAMP/T is designed to replace the old Hawk and Sidewinder air defense systems and meet the needs of modern land defense for medium-range systems capable of operating in new combat scenarios, characterized by factors such as reduced reaction time to air threats, high mobility and the possibility of adapting the equipment to the dynamics of modern battlefields.
SAMP/T began full-scale development in 1990, production began in 1997, and tests were carried out in 1999. The first test of the entire system was carried out in July 2005, during which SAMP/T successfully captured, tracked and intercepted his target. In May 2008, the system began operational evaluation with the Italian and French armies, and two successful test launches were carried out. SAMP/T entered service in France in 2010 and in Italy in 2013. In October 2010, the system intercepted a short-range ballistic missile for the first time, after which the French Air Force conducted a second interception test in November 2011.
Its first operational deployment took place in February 2011 at the G8 summit in Deauville, France, while in March 2013, the Italian Army and the French Air Force deployed the system for the first time in the NATO anti-missile defense architecture (Active Layered Theater Ballistic Missile Defense System), again successfully intercepting a long-range ballistic missile during testing.
On January 22, 2023, Italian Foreign Minister Antonio Tajani confirmed that Italy will deliver a batch of SAMP/T to Ukraine together with France, and he also announced that the transfer is being finalized.
The SAMP/T system includes a command and control vehicle, an engagement vehicle, a radar vehicle equipped with Arabel radar and up to six transport vehicles, with eight interceptors and a full set of charging equipment in the ground module, including a power generation vehicle with two generator sets.
The Arabel 30 multi-purpose radar is a 3D phased array radar developed by Thales with an identification friend or foe system that provides 360-degree coverage. SAMP/T can track up to 100 targets and attack 10 of them simultaneously.
The maximum range of the Asterl5 and Aster30 missiles used by SAMP/T can reach 30 kilometers and 120 kilometers respectively, but for short-range ballistic missiles and anti-radiation missiles, this range will drop to 15 kilometers. Both interceptors use two-stage solid propellants. Aste130 is 4.9 meters long, 0.18 meters in diameter and weighs 450 kilograms. It can fly at a speed of up to Mach 4.5 and a flight altitude of up to 20 kilometers. In 2016, Eurosam began to develop an extended-range improved model called Aster30Block 1Nt (New Technology) Extended Capability. The upgraded missile is equipped with a new seeker that works in the Ka band instead of the Ku-band seeker used previously.
The Aster family of air defense interceptors is extremely maneuverable. The latest target data transmitted by the multi-function radar is used for mid-flight guidance and data updates. During the guidance phase, the missile is guided by its active seeker, which can also detect stealth cruise missiles. The Aster 30 interception is very accurate. In 70% of the test shots, they successfully intercepted the target. Once identified and tracked, the target is hit by shrapnel detonated by the proximity fuse trigger.
The SAMP/T system can adapt to various long-range radars. When using the Thales GM400 long-range radar, the detection range is between 300 and 400 kilometers. The launch vehicle can be placed 25 kilometers away from the radar. The system uses the Link16 data link that meets NATO standards, so SAMP/T is fully interoperable with other alliance partners. It only requires 14 people to deploy and operate, and the deployment and withdrawal time is very short, with strong battlefield survivability.
The SAMP/T system equipped with the ASTER30 missile is a key element of modern air defense and is known for its ability to intercept threats at ranges of 120 kilometers and 20 kilometers. The system’s radar is capable of tracking and engaging multiple targets simultaneously, providing a comprehensive 360-degree defense capability. This versatility enables it to defend against a wide range of air threats, including aircraft, cruise missiles, and tactical ballistic missiles, making it an essential component of both homeland and mobile air defense networks. .
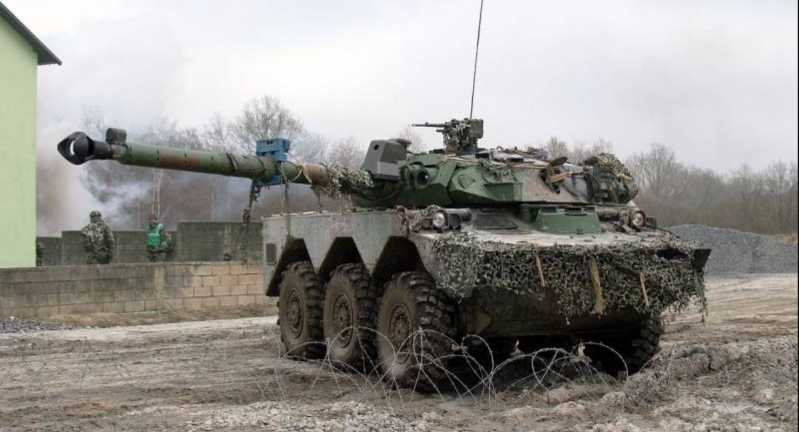
AMX-10RC reconnaissance vehicle (38 units delivered)
AMX-10RC wheeled armored reconnaissance vehicle, produced at the Issy-Lay-Moulineaux manufacturing plant in France, is mainly to meet the needs of the French Army to replace the Panhard EBR wheeled reconnaissance vehicle. The French Army began to submit orders in 1976, and the French Army purchased a total of 284 vehicles. This type of armored vehicle was also recommended to the US light troops.
AMX-10RC wheeled armored reconnaissance vehicle basic parameters: total length 6.24 meters, total width 2.78 meters, total height 2.56 meters, combat weight 14.8 tons, the power system is a Hispano-Za HS115 diesel engine (the last two batches of AMX-10RC reconnaissance vehicles may be replaced with Baudouin 6F11SRX diesel engines), rated power 280 horsepower, with a certain degree of amphibious capability, maximum water speed of 7.2 kilometers per hour, maximum driving speed of 85 kilometers per hour, and maximum cruising range of 1,000 kilometers.
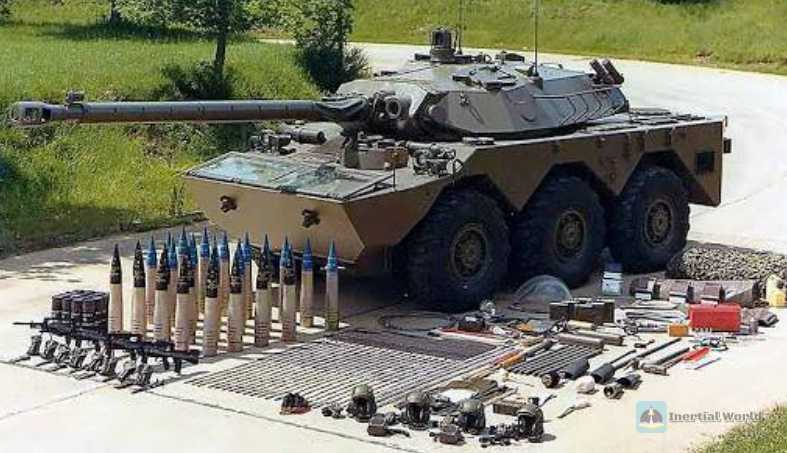

The layout of the vehicle body is that the cockpit is in the front, the turret is in the middle, and the power compartment is in the rear. It adopts a three-person turret. The commander and gunner are located on the right side of the turret, and the loader and radio operator are on the left. It is designed with hydraulic pneumatic suspension and adjustable pneumatic wheels. The hydraulic cylinder acts as a spring and shock absorber, and the height of the bottom of the vehicle from the ground can be adjusted, which is convenient for firing shells in different combat environments.
The main weapon is a GIAT F2 type 105mm rifled gun with a 48-caliber, equipped with a recoil machine and semi-automatic loading. The gun body has a muzzle brake and a thermal jacket. It can fire armor-piercing shells, grenades, and tail-stabilized armor-piercing shells. It reacts quickly and can fire after 10 seconds, but it is not designed with a two-way stabilizer and does not have the ability to fire while moving. There are 38 rounds of ammunition.
The effective range of the gun exceeds 2,000 meters. It can fire armor-piercing shells, armor-piercing shells, smoke bombs and grenades. When firing the OLF 105 F3 tail-stabilized armor-piercing shell, it can penetrate the NATO three-layer heavy standard target plate at a distance of 2,000 meters, which is equivalent to a 40Cr steel plate with a thickness of about 800 mm. However, due to the wide rifling pitch of the gun, its flight stability and accuracy are low. At the same time, it is equipped with a coaxial 7.62 mm machine gun with 4,000 rounds of ammunition.
The vehicle is equipped with a commander’s periscope, and the loader has three periscopes in front, left and rear. The commander has a panoramic periscope group consisting of 6 periscopes. The fire control system is the advanced M504 telescope and the electronically controlled optical compensator with automatic input of shooting correction values, M550 laser rangefinder and M553 gun bore sight. In addition to the day and night sight, the gunner is also equipped with a DIVT13 low-light television system for night operations. The commander is equipped with a panoramic M389 telescope.
The body and turret are made of fully welded aluminum armor, and can be equipped with additional armor and grille armor. It can withstand large-caliber bullets, howitzer fragments and rocket launchers. The front armor can withstand 20mm artillery shells and 12.7mm large-caliber machine gun bullets within a range of 300 meters. The vehicle is equipped with air conditioning, a slightly overpressure heater in the combat compartment, three-defense devices, night launch control system, navigation system and floating equipment to enhance its battlefield survivability.
A M X-10RC is an armored wheeled vehicle equipped with a 105mm gun, capable of engaging targets at a distance of 2,000 meters. Its versatility lies in its all-terrain mobility and strong armor protection against small arms and shell fragments, making it suitable for reconnaissance missions, light combat missions, and providing fire support for infantry units. The version provided to Ukraine is the AMX-10RCR, an upgraded version of the earlier AMX-10RC. They received 9,000 rounds of ammunition.
The subsequent modernized and upgraded version, named AMX10RCR, mainly focuses on armor, mobility and firepower as well as digitalization. It can fire new high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shells, and is equipped with new additional armor, an extended turret tail, a new gearbox and a hydraulic pneumatic suspension electronic monitoring system, an infrared countermeasures system, and the most important digital aspect is the setting of a battlefield management system and an automatic monitoring system VOPI, the main purpose of which is to exchange digital data between the vehicle and the squadron command vehicle, while strengthening the three defense systems.
VAB armored vehicle (250 units delivered)
VAB armored transport vehicle (English: VAB Wheeled armored carrier) is an armored transport vehicle developed by Renault and GIAT in France in the 1970s based on orders from the French Army.
The vehicle has two designs: four-wheel and six-wheel. The two designs have the same body layout, but the size is different. The same parts also include the power unit, control mechanism, differential, braking system and other components and systems. Commercial vehicle components are widely used in production.
In order to meet the needs of the French army, about 4,000 VAB 4x4 models were produced, while the 6x6 model is an export model. There are about 5,000 VAB armored transport vehicles in the world.
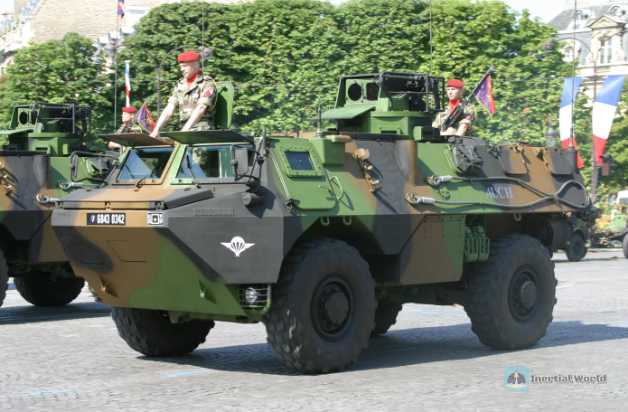

The combat weight of the VAB armored vehicle is 14.2 tons (6x6) and 13 tons (4x4), with 2 crew members and can carry 10 infantrymen. The body is divided into 3 main parts. There are 2 side doors and 2 top hatches in the front. The driver is on the left, with a three-proof filter installed next to him, and the commander (also a machine gunner) is on the right. He can use different weapons according to different models. In front of them, there are two bullet-proof windshields, which can be covered with baffles hinged to the top when necessary. The engine, a main fuel tank with a capacity of 300 liters and a fire extinguishing system are installed on the left side of the middle part. The inlet and outlet shutters are located on the roof, and the exhaust pipe is located on the right side of the roof. There is a passage connecting the front and rear compartments. There is also a special partition in the middle part for sound insulation and heat insulation. There are 10 infantrymen in the rear. There are three windows on each side of the vehicle. When the windows are open, infantry can use light weapons to shoot. The interior space is 6.5 cubic meters, which is almost half of the vehicle volume. It has three top hatches, two rear doors and eight observation windows (three on each side and one on each rear door). The rear passenger compartment is 2.46 meters long, 1.375 meters wide and 1.35 meters high, with a total area of 3.38 square meters, and can carry 2,000 kilograms of cargo.
Behind the cockpit is the engine-transmission compartment. At the rear of the vehicle is the troop compartment, which can accommodate six fully armed soldiers. Soldiers get off from the two rear doors. The vehicle can be equipped with ventilation and filtration devices, heating systems and protection systems for weapons of mass destruction, additional armor, night vision equipment and tire centralized inflation systems.
The French army is equipped with VAB/VTT (4x4) standard models. The weapon is a CB52 rotating turret and a 7.62mm machine gun installed on the top deck above the commander. The machine gun has an elevation range of -15°~+45°, and an elevation range of -20°~+80° for air defense. In addition, the base vehicle can also be equipped with a TLi52A turret, with an M2HB12.7mm machine gun, etc. The body is welded from steel plates and can defend against 7.62mm bullets and shrapnel within a distance of 100 meters. The power of the VAB armored vehicle was originally a D2356HM72 6-cylinder in-line water-cooled diesel engine developed by MAN Company of the Federal Republic of Germany, with a cylinder diameter of 123mm, a stroke of 150mm, and a total displacement of 10.7L. When the engine is at 2200r/min, the maximum power is 162 kW (220 horsepower); at 1600 rpm, the maximum torque is 784 Nm. The cooling fan is driven by a hydraulic pump and motor with constant temperature control, which can reduce the power consumption of the fan and ensure rapid preheating when the engine is started.
Since 1984, the MIKS06.20.45 162 kW (2200 horsepower) 6-cylinder water-cooled turbocharged diesel engine produced by Renault of France has replaced the MAN engine.
The VAB vehicle has sufficient floating ability on the water. When driving on the water, the front wave shield of the vehicle is erected, and the water jet propellers on both sides of the rear of the vehicle are used for propulsion. The power is drawn from the rear axle through the short shaft and the bevel gear. The water jet propellers are all equipped with a pivot cover (deflector) that can change the direction of the water flow and enable the vehicle to turn in the water. The driver controls the water jet propeller designed by Dowty of the United Kingdom and produced by Messier of France through a small electro-hydraulic joystick. Two electric drainage pumps are also installed at the bottom of the vehicle.
VAB is also equipped with navigation, heating, ventilation and other equipment, and the windshield is also equipped with heating resistors to prevent ice formation. Optional equipment includes grenades, armored grenade throwing holes, air conditioning equipment, holes with observation mirrors, gas removal devices, three-proof devices, infrared or passive night vision devices, sound amplifiers and front winches for climbing steep river banks (winch pulling force 68.6 kN, steel rope length 60 meters). The models equipped by the French army have three-proof devices, which include filters and electric fans with a flow rate of 3 cubic meters/minute.
VAB 4x4 armored personnel carriers are specially designed to transport troops while defending against small arms fire and shell fragments. It has a configuration that can adapt to roles such as command, medical evacuation and logistics, with a payload capacity of up to 2 tons and a maximum speed of about 90 kilometers/hour, ensuring multi-functional combat assistance.
VLTT P4 off-road vehicle (120 units delivered)
VLTT P4 is a flexible off-road vehicle known for its excellent mobility and reliability in missions such as personnel transportation, reconnaissance and logistical support. Designed to accommodate 4 people, with a payload capacity of approximately 500 kg and a speed of up to 100 km/h, the P4 demonstrates versatility in various military and support functions in different terrains.

Finally, it can be added that 1,000 FAMAS assault rifles and 560 heavy machine guns have been delivered. The accompanying ammunition is nearly 3 million rounds of bullets.